LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
DOI 10.25176/RFMH.v19.n2.2074
1 Medical Student Faculty of Medicine, Ricardo Palma University, Lima-Peru.
a Medical Student.
Dear Editor
Gallbladder cancer is one of the most common pathologies of the digestive tract. It is more frequent in women than in men predominantly in the sixth and seventh decades of life. In white populations, it is a type of neoplasm that ranks fifth worldwide1.
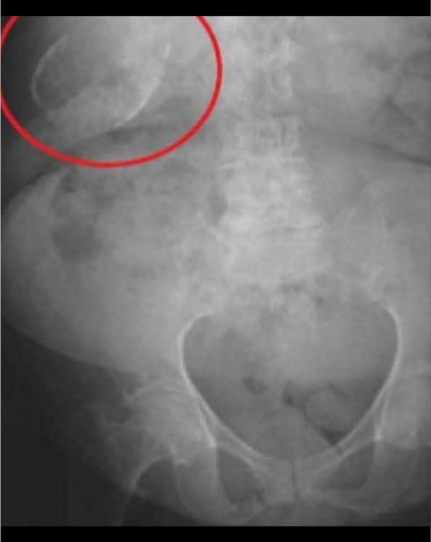
Usually, gallbladder cancer causes no signs or symptoms until later in the course of the disease, when the tumor is large or has spread. The vesicular pathology has been increasing over the years since there is no proper prevention. Many of the risk factors, such as age, sex and others that vary like diabetic women, smoking, obesity with the presence of stones2.
Chile has the highest incidence of vesicular cancer, between men and women. According to the study of Eslick published in 2010, the rate of the registry of the city of Valdivia is 12.3 and 27.3 in men and women per 100,000 inhabitants, placing it with the highest incidence in the world - data from the Ministry of Health of Chile3.
In 2010-2012 according to the INEN - MINSA (National Institute of Neoplastic Diseases - Ministry of Health), in metropolitan Lima, there were 1284 cases of gallbladder cancer. The population most affected by this pathology were adults older than 75 years old. By age group and sex, it was predominant in women, increasing from 3.2% in women from 55 to 74 years to 3.5% in 75 years to more4.
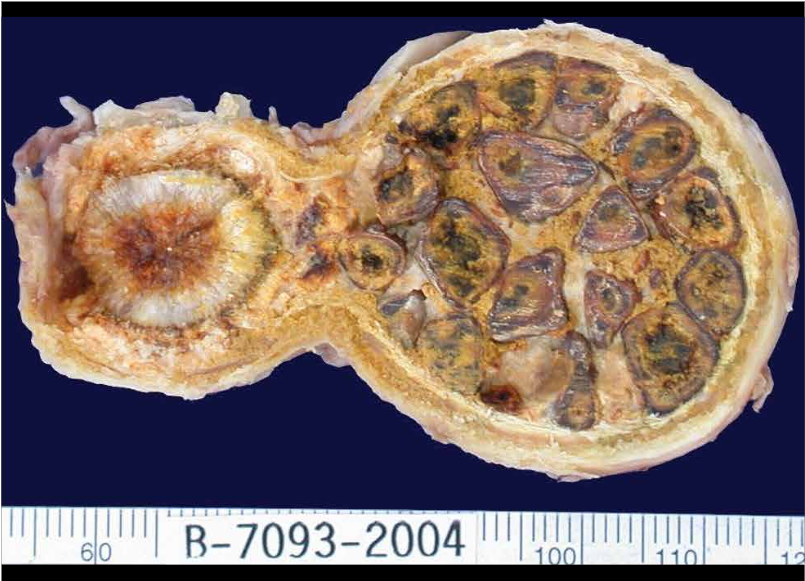
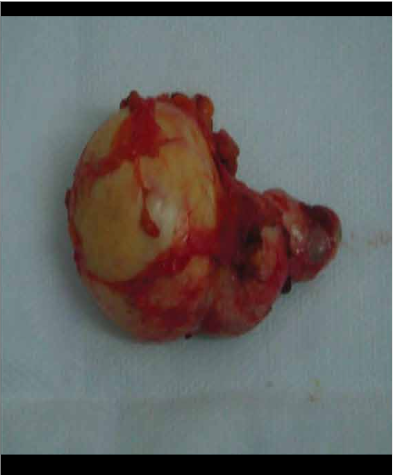
The onset of symptoms is insidious and simulates cholecystitis; often the diagnosis is established during gallbladder surgery from other cause. About 80-90% of people with gallbladder cancer have cholelithiasis. It is believed that, due to its ability to produce chronic irritation of the vesicular mucosa, cholelithiasis participates in the development of cancer. This cancer is unresectable at the time of diagnosis and the average survival at five years has been 1% for many years. Gallbladder cancer is the most frequent malignant tumor of the bile ducts1.
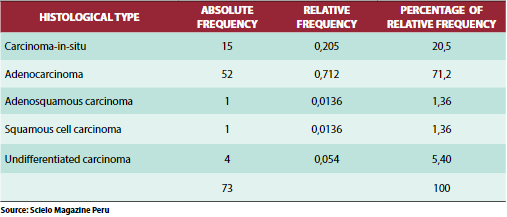
In an analytical observational study, cross-sectional and retrospective that was performed in the surgical service of the Hospital Regional Honorio Delgado (HRHD) of Arequipa during the period from January 2008 to June 2010, the population consisted of all patients who attended the service of surgery that underwent surgery, the operative piece was sent to the pathology department for processing. The criterion was to have a result (report) of pathology.There was evidence that 73 patients had a diagnosis of gallbladder cancer. The most common histological type was adenocarcinoma with 71.2% (52 cases), followed by in-situ carcinoma with 20.5% (15 cases), both histological types representing 91.7%. Undifferentiated carcinoma was present with 4 cases5.
The present communication seeks to identify the clinical and epidemiological factors related to vesicular cancer; in addition, it identifies which type according to the pathological anatomy is the most prevalent; as well as taking into account the most frequent sociodemographic profile in overweight or obese women
Correspondence:Kelly Regina Huacachi Trejo.
Address::Jr. Los Laureles 352. Dpto. 402. Santiago de Surco.
Telephone:+51 999115611.
E-mail: kelita_bht¬@hotmail.com
