EDITORIAL
DOI 10.25176/RFMH.v19i3.2176
1 National Center for Epidemiology, Disease Prevention and Control - MINSA, Lima-Peru.
2 Biomedical Sciences Research Institute (INICIB), Ricardo Palma University, Lima-Peru.
3 General Director of INICIB, URP, Lima-Peru.
a Specialist in Epidemiology.
b Specialist in Clinical Oncology.
c Doctorate in Public Health.
d Doctorate in medicine.
Measles, considered among the most contagious transmissible infections due to its high potential epidemic risk of transmission, remains a focus of concern in the world due to the increase in cases and its consequent morbidity and mortality1. The rash usually starts on the face, and in a centrifugal way it spreads to the trunk and extremities. Although the disease determines a strong humoral and cellular immune response stimulating specific immunity for life, it also produces an important immunosuppression that lasts several weeks increasing the susceptibility to secondary infections2.
Measles was considered eliminated from the Americas since 2002 due to the absence of endemic transmission of the disease in the region; achievement achieved by regional efforts to achieve high vaccination coverage through regular immunization programs and mass vaccination campaigns. However, until April 2019 the Pan American Health Office reported that 12 countries reported confirmed cases: Argentina, Bahamas, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, United States of America, Mexico, Peru, Uruguay and Venezuela. 09 countries reported cases imported from countries outside the region with different genotypes. Also, between January 1 and April 11, 2019, 5556 cases of measles were confirmed in 20 States of the United States3.
The increase in travel and international trade, as well as the appearance of measles transmission threats associated with population migration from areas where vaccination rates are below the levels to prevent the spread (95% measles coverage) and that children receive two doses of the measles vaccine before their fifth year of life) has made this disease a priority on the public health agenda. Thus, in the framework of the International Health Regulations (IHR), the communications of the National Liaison Centers have been intensified in the detection, follow-up and control of suspected and confirmed cases of measles entering or leaving the countries with the purpose of public health interventions are carried out to mitigate and reduce the risk of the spread of cases entering the border areas.
Thus, in 2018, in Peru, 42 cases of measles, imported or related to imports, were confirmed. No deaths were recorded. 26% (11) of the cases were less than 1 year. The confirmed cases came from Amazonas, Callao, Cusco, Ica, La Libertad, Lima, Piura and Puno and the entry routes of these patients were via terrestrial, aerial and fluvial (Figure 1). During the year 2019 in Peru, a case of measles was confirmed that corresponds to a woman of 40 years, Peruvian from Spain who entered Peru on March 21. Home rash on April 1, was hospitalized for pneumonia. No cases were detected secondary to this case3.
In this context, PAHO is recommending5: (a) Carry out vaccination campaigns to maintain homogeneous coverage of 95% with the first and second doses of the vaccine against measles, rubella and mumps; (b) identify and vaccinate populations at risk, such as health personnel, people working in tourism and transportation (hotels, airports, taxis and others); (c) identify the external migratory flows (arrival of foreign persons) and internal (displacement of population groups) in each country, according to the national scheme; (d) implement a plan to immunize the migrant population in high traffic borders, prioritizing the population at risk, both migrant and resident in the districts that house these population groups; (e) provide a rapid response to imported cases of measles to prevent the reestablishment of endemic transmission.
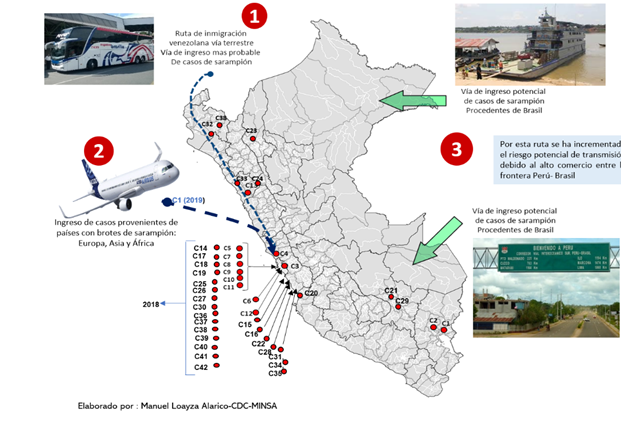
Figure 1. Measles case entry routes 2018-2019, Peru.
Citar como: Manuel J. Loayza-Alarico, Jhony A. De La Cruz -Vargas. Sarampión amenaza reemergente de epidemia en el Perú. Rev. Fac. Med. Hum. Julio 2019; 19(3):7-8. DOI 10.25176/RFMH.v19i3.2176
