REVIEW ARTICLE
REVISTA DE LA FACULTAD DE MEDICINA HUMANA 2020 - Universidad Ricardo PalmaDOI 10.25176/RFMH.v20i4.2946
GENETIC BASES OF PULMONARY ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION
BASES GENÉTICAS DE LA HIPERTENSION ARTERIAL PULMONAR
María del Carmen Castro-Mujica1,a, Hugo Abarca-Barriga1,a
1Facultad de Medicina Humana – Universidad Ricardo Palma, Lima-Perú
aClinical Geneticist
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a heterogeneous disease where Genes play a vital role. Hereditary PAH (HPAH) is defined as a genetic condition with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, incomplete penetrance, variable expressiveness, presenting a phenomenon of anticipation and grouping the cases of familial PAH defined by the presence of two or more members of the family with PAH with or without identified germline variant and cases of idiopathic PAH corresponding to isolated cases in the family with an identified germline variant. It is necessary to confirm the diagnosis in at least two relatives (FPAH) or determine the germ variant in an isolated case in the family (IPAH) to establish the diagnosis of HPAH.
Keywords: Pulmonary hypertension; Genetic counseling (Source: MeSH NLM).
RESUMEN
La Hipertensión arterial pulmonar (HAP) es una enfermedad heterogénea donde los genes juegan un rol sumamente importante. La HAP hereditaria (HAPh) se define como una condición genética de patrón de herencia autosómico dominante, de penetrancia incompleta, de expresividad variable, que presenta un fenómeno de anticipación y que agrupa a los casos de HAP familiar definido por la presencia de dos o más miembros de la familia con HAP con o sin variante germinal identificada y a los casos de HAP idiopática que corresponde a los casos aislados en la familia con una variante germinal identificada. Para establecer el diagnóstico de HAPh, es necesario confirmar el diagnóstico en al menos dos familiares (HAPf) o identificar la variante germinal en un caso aislado en la familia (HAPi).
Palabras Clave: Hipertensión pulmonar, asesoramiento genético (fuente: DeCS BIREME).
Initially, pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) was classified as primary PAH from 1950 to 1998, where the diagnosis was made by exclusion after determining the absence of identifiable causes or known risk factors(1).
Hereditary PAH (HPAH) is a recently adopted term defined as a complex genetic condition, with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern (AD), with incomplete penetrance influenced by gender, variable expressiveness, and presenting a phenomenon of anticipation.
HPAH includes cases of familial PAH (FPAH) defined by the presence of two or more members of the family with PAH with or without an identified germline variant, and cases of idiopathic PAH (IPAH) corresponding to isolated cases in the family with an identified germline variant(1-3). These last cases could compare to cases in which the disease has not yet manifested due to low penetrance or de novo variants. PAH corresponds to approximately 94% of all PAH cases, while the remaining 6% corresponds to FPAH cases(4), both clinically and histopathologically indistinguishable(1).
The BMPR2 gene (bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2), which encodes bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2 (BMPR-II) and which belongs to the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-B) superfamily, has been identified in 70-75% of cases of PAHf and 10-40% of cases of PAHi, being considered the main genetic determinant of PAH(1). There are other genes involved in the pathogenesis of PAH, such as ACVRL1, CAV1, KCNK3, ENDG, SMAD9, BMPR1B, among others, but they are less frequent (1-3%)(5).
HPAH has a greater severity of the disease in patients who carry variants in the BMPR2 gene than those who do not carry the mutation, which are associated with “missense” variants in the BMPR2 gene(6-8). In addition, cases of PAH carrying variants in the BMPR2 gene that present an anticipation phenomenon have been identified, defined as the presentation of the disease at an earlier age in the following generations(3,9), however there are still no systematic studies of demographic, base that have been carried out to avoid evaluation bias in these cases(10).
Currently, knowledge of genetics and molecular biology allows us to understand the mechanisms and molecular pathways involved in HPAH, the objective of this review being to provide the necessary scopes for its better understanding in order to provide the patient with an adequate genetic diagnosis, a specialized treatment and, above all, the corresponding genetic counseling, which allows you to be informed about the genetic-molecular studies available for the identification of germline mutation carriers and to be able to carry out individualized management and monitoring of the patient and their asymptomatic carriers at risk.
FPAH AND THE DISCOVERY OF THE BMPR2 GENE
FPAH was first described in 1951 by Dresdale et al(11). In 1997, using a linkage study, using microsatellite markers distributed throughout the genome, which required a large number of families of patients and controls to compare the frequency of genotypes in both groups and determine the association between disease and marker, the 2q31-32 locus was identified as the region where the gene causing FPAH would be located(12,13). Subsequently, in 2000, the candidate genes were sequenced and the BMPR2 gene was identified as the main genetic cause of FPAH(14-16). The search for candidate genes related to the signaling pathway of the BMPR2 gene continues to be the subject of study to understand the molecular pathogenesis of FPAH(17).
After its discovery in the cases of FPAH, the BMPR2 gene became the candidate gene for the cases of IPAH since the phenotypes were identical, which led to a study of 50 patients with IPAH, where 13 of them (25% ) were carriers of variants in the BMPR2 gene(18). The apparently sporadic PAH, corresponding to isolated cases in the family, without a family history, harbor germline variants in the BMPR2 gene in 10-40% of cases, thus constituting a risk of hereditary transmission to developing PAH in others members of the family; while FAPH, with a family history with or without identified germ variants, present germ variants in the BMPR2 gene in 70% of cases(16,19-22).
Currently with the development of new technologies, such as next-generation sequencing, we can identify, on a large scale, common variants in various genes that would be involved in the genetic predisposition to develop PAH.
CLASSIFICATION OF PAH
The classification of Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) has been changing over the years. Thus, the first classification was proposed in 1973, where the categories of primary pulmonary hypertension (PPH) and secondary pulmonary hypertension (PSH) were designated, according to the presence or absence of identified risk factors(23,24). In 1998, during the Second World Congress on Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) held in Evian, France, a PAH classification was proposed based on the clinical data of the patients to individualize the categories that shared similarities in pathogenesis, clinical characteristics and therapeutic options(25).
Subsequently, in 2003, during the Third HP World Congress in Venice, Italy, essential changes were proposed such as eliminating the term “Primary Pulmonary Hypertension” and incorporating the terms “idiopathic PAH” and “familial PAH”(26). In 2008, during the Fourth HP World Congress in Dana Point, USA, the international group of experts reviewed the previous classification. It was proposed that the term “familial PAH” be replaced by “hereditary PAH”(2). That group 1 included five subgroups corresponding to PAHi, HPAH, PAH induced by drugs and toxins, PAH associated with other diseases, and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn(27,28). In the last HAP classification, established in 2013 during the Fifth World Congress of HP in Nice, France, some minor modifications were proposed without altering the previously established structure(19).
PAH IN CHILDREN
PAH in children is more severe and refractory to treatment. It has differences in its presentation since two age peaks at diagnosis have been described, one before the first year of life and the next at approximately twelve years of age(29,30). Patients who carry variants in the BMPR2 gene, present the genetic alteration from their conception; however it is not yet explained because some cases the disease develops in children and in other cases in adults, which suggests that there would be other factors that would influence at the age of presentation of PAH(31,32).
PAH in pediatric patients is more heterogeneous than in adults and can be associated with various genetic syndromes, especially those with congenital heart disease, vascular disease, and liver disease(10).
PAH in children has multiple genetic etiologies compared to PAH in adults, and although it is a rare complication of some genetic syndromes, it can be found in Down syndrome and other genetic syndromes but not necessarily associated with congenital heart disease and PAH. as in DiGeorge syndrome, VACTERL, CHARGE, Noonan among others(10,17). Other genetic syndromes associated with PAH, but not usually associated with congenital heart disease, include Adams-Oliver syndrome, neurofibromatosis 1, long QT syndrome, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Cantu syndrome, Gaucher disease, and glycogen storage diseases(10,17).
HPAH has an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, with incomplete penetrance where approximately only 20% of carriers of a germinal variant in the BMPR2 gene will develop the disease, which suggests that the gene variant is necessary but not sufficient to express disease and that may require other genetic and/or environmental factors to contribute to its development(5,29,33).
Female sex is the best-demonstrated factor influencing PAH penetrance, with a female: male ratio of 3: 1 in PAH of different etiologies, including PAHi, PAHf, and PAH associated with other pathologies (PAHa)(8,14,34), it is also estimated that penetrance varies according to gender, being approximately 10% in men and 30% in women(35).
The predominance in women, the reduced penetrance, and the variable age at diagnosis of PAH has been the subject of study, and various publications have suggested that estrogen metabolism is a key element in the penetrance of PAH(35-37) for which reason they have compared the clinical aspects between patients with PAH carrying variants in the BMPR2 gene and patients without an identified mutation, according to gender.
Most women metabolize estradiol (E2) into 2-estrogen (2-OHE), and some metabolize E2 to 16-estrogen (16a-OHE), which stimulates cell proliferation by constitutive activation of estrogen receptors(35). In addition to being more mitogenic than 2-OHE, 16a-OHE can be more genotoxic, and patients who metabolize a large proportion of E2 to 16a-OHE increase their risk of developing the disease due to these effects(36). In patients who carry variants in the BMPR2 gene, the development of the disease is strongly related to a decrease in the 2-OHE / 16a-OHE ratio, associated with a decrease in the expression of the cytochrome that metabolizes estrogens, Cytochrome p450 1B1 (CYP1B1), and polymorphisms in it(36). Some studies have shown a significant decrease in the levels of CYP1B1 transcripts in affected women carrying variants in the BMPR2 gene compared to unaffected carriers(37). Estrogens have been proposed as possible disease modifiers due to their lower prevalence in prepubertal women(38), and being potent mitogens of smooth muscle cells of the pulmonary vasculature(39). Other studies have also proposed that TGFb1 gene polymorphisms cause an imbalance in the TGF-B signaling pathway, influencing the penetration of BMPR2 mutations and modulating the age at PAH(1,36,40).
ANTICIPATION PHENOMENON IN PAH
The phenomenon of genetic anticipation, that is, the development of PAH at an earlier age and with greater severity in subsequent generations(41,42), has been evidenced in various studies; However, they could not be explained by trinucleotide expansion phenomena or progressive telomere shortening as occurs in other diseases(43), so long-term follow-up studies may be necessary to make appropriate and statistically significant comparisons(44)
GENETIC-MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS IN PAH
The application of molecular biology in the study of cases of PAH, allows us to establish its genetic-molecular diagnosis, as well as to contribute new knowledge in research on its pathogenesis.
The BMPR2 gene encodes the BMPR-II protein that is expressed in lung endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells mainly, regulating multiple functions such as proliferation, migration, differentiation, and cell apoptosis, and is also a member of the superfamily of TGF-ß receptors(41). Members of the TGF-ß superfamily are subdivided into several families, which include TGF-ß ligands, receptors, and accessory molecules, activins, and the largest of these groups corresponds to bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs)(21).
To date, 300 different variants have been identified in the BMPR2 gene in 75% of FPAH, the majority being “nonsense” variants that lead to haploinsufficiency(10) and are identified by gene sequencing after detection of point variants And if no variant is detected, the study of large gene rearrangements is carried out as a complementary method, such as the deletion/duplication analysis by MLPA (multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification) or other similar methods(5,45), however, in the remaining 25% the variants responsible for the disease have not yet been identified(20)). Regarding the cases of IPAH, we have identified mutations in the BMPR2 gene in 10–40% of cases(5). And finally, regarding other genes involved in PAH and that are also part of the signaling pathway of the TGF-B superfamily, mutations have been identified in ACVRL1 (ALK1), ENG, SMAD4, SMAD9, CAV1, BMPR1B (ALK6)(7,10,32,46-51), which emphasizes the importance of this pathway in the integrity of the pulmonary vasculature.
Several studies show that carriers of variants in the BMPR2 gene, compared to non-carriers, present a more severe form of the disease, with an earlier age of onset and more significant hemodynamic compromise at the time of diagnosis and more prone to lung transplantation(6,9)..
The genetic-molecular study should be offered to all patients with PAH and PAH, explaining the importance of determining the presence of germline variants in them for the subsequent search for the specific variant in other members of their family in less time and at a lower cost than the first case. identified(5). With the development of gene panels, costs have been reduced, and patients’ accessibility to perform them has increased compared to the individual study of each gene.
MOLECULAR ROUTE OF BMPR2
Patients with PAH who carry variants in BMPR2 present the disease approximately 10 years earlier than non-carriers and have a more severe hemodynamic compromise at diagnosis(9), which has led to the study of the BMPR2 gene and the pathway molecular by which it acts.
The BMPR2 gene contains 13 exons(22) and encodes the BMPR-II protein of 1038 amino acids, which comprises an extracellular ligand-binding domain (exons 2 and 3), a transmembrane domain (exons 4 and 5), a domain highly conserved catalytic kinase (exons 6 to 11) and a cytoplasmic domain (exons 12 and 13)(52). So far, of the more than 300 different variants identified, 30% are located in exon 12(53).
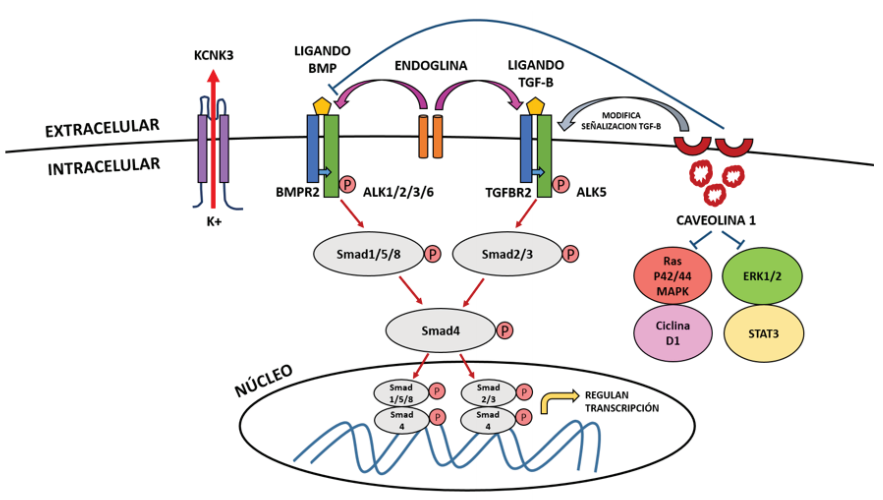
BMPR-II is a receptor of the family of cytosines known as bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), and as a member of the TGF-β receptor superfamily, BMPs play a crucial role in the regulation of lung morphogenesis(43). Normally BMPs regulate cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis through an intracellular signaling cascade through cytoplasmic signaling proteins called Smads. The Smad family of proteins are responsible for transforming TGF-B receptor signaling and regulating gene expression(54).
To understand the mechanism by which variants of the BMPR2 gene lead to HPAH, TGF-B signaling must be understood. Signaling through BMPRII, like other TGF-B receptors, involves the binding of BMP as a ligand to a type I receptor (BMPR-I) that associates with an active type II receptor (BMPR- II) at the cell membrane, this BMPR-II phosphorylates the BMPR-I receptor and initiates a cascade of successive phosphorylations involving Smad proteins that normally participate in inhibiting cell growth and inducing apoptosis. Of these proteins, Smad 1, 5 and 8 are first phosphorylated, which then form a complex with Smad 4 and then translocate to the nucleus to regulate gene transcription in conjunction with specific nuclear cofactors and repressors(43,55) (figure 1).
Variants in the kinase domain of BMPR2 initiate constitutive signaling downstream of Smad molecules in lung smooth muscle cells, causing pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic effects that promote the development of PAH(43), therefore it is postulated that these variants in the BMPR2 gene eliminate the regulatory function of the growth of pulmonary vascular cells by disrupting the activation of Smad.
The BMP ligand binds to the type II receptor (BMPR2) at the cell membrane level, which phosphorylates the type I receptor (ALK1, ALK 2, ALK 3 or ALK 6), triggering the phosphorylation of Smad 1, Samd 5, Smad 8 , which phosphorylate Smad 4 to later form a complex and translocate to the nucleus, where they modulate gene expression. This mechanism is similar to what happens when the TGF-B ligand binds to the type II receptor (TGFBR2), which phosphorylates the type I receptor (ALK 5), triggering the phosphorylation of Smad 2 and Smad 3, which phosphorylate Smad 4 and translocate to the nucleus. Endoglin is an accessory membrane glycoprotein that interacts with signaling receptors for BMP and the TGF-B superfamily. Caveolin 1 normally buffers BMP signaling after inhibiting its receptor to prevent vascular proliferation, but in its absence it causes activation of the STAT3 and ERK1 / 2 signaling pathways and the Ras / p42 / 44 / MAPk and Cyclin D1 pathways. It also modifies the TGF-B signaling pathway by providing a link between CAV1 and BMPR2 mutations in the molecular pathogenesis of PAH. KCNK3 is a potassium channel (K +) protein in the smooth muscle cells of the pulmonary arteries and its activation causes K + leakage to the extracellular, membrane hyperpolarization and vasodilation.
MECHANISMS OF HAPLOINSUFFICIENCY AND DOMINANT NEGATIVE
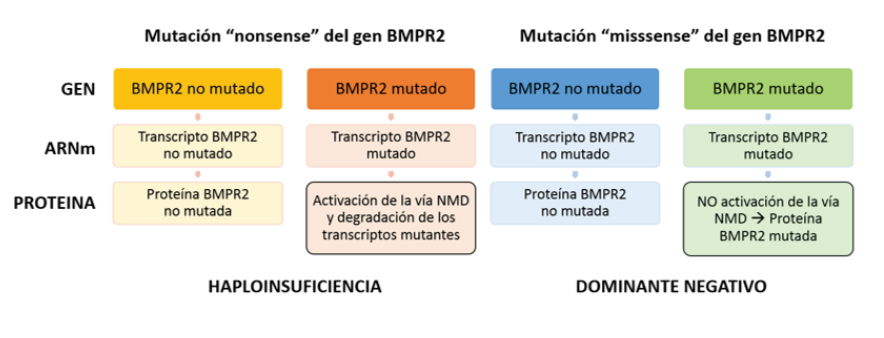
Heterozygous variants in the BMPR2 gene are the main risk factor for the development of HPAH. However, carriers have a 20% penetration, which has allowed investigating of other factors that may influence disease expression(6,40). Variants that generate an amino acid different from the original can be of the type "missense variants" ("missense") and "nonsense variants" ("nonsense") that generate a signal to stop the reading of mRNA by ribosomes(43). Approximately 70% of the pathogenic variants reported in the BMPR2 gene are “nonsense,” “frameshift,” defects of the “splicing” site, and gene rearrangements that lead to a decrease in its activity(43). The remaining 30% corresponds to "missense" variants causing amino acid substitution in critical functional domains of the receptor (e.g., ligand binding, kinase domain)(20,56,57).
The "nonsense" variants in the BMPR2 gene result in a truncated protein and have a different impact than the "missense" variants because they have differences according to the activation of the NMD pathway(58). The NMD (Nonsense-mediated decay) pathway is a cellular mRNA surveillance mechanism by which the truncated mRNA produced by a “nonsense” variant is detected and eliminated by the cell (NMD positive variants), preventing the translation of harmful transcripts, which results in a haploinsufficiency effect due to insufficient amount of functional protein but with the persistence of the remaining normal protein produced by the non-mutated allele(59,60).
Haploinsufficiency is the generally accepted molecular mechanism to explain how the transcript expression of the non-“mutated” allele of the BMPR2 gene influences the reduced penetration of the disease(60). In contrast, "missense" variants are resistant to destruction by NMD mechanism (NMD negative variants), producing a mutant protein with harmful effects that also completely blocks the activity of the remaining protein of the non-mutated allele, creating an effect called " dominant negative”(22,43,61) that causes a more severe expression of the disease, with an earlier age at diagnosis and death, as well as a shorter survival(1,6,60,62-65). (figure 2). In a study carried out, it was found that most of the “missense” variants corresponded to patients under 36 years of age, while most of the carriers of “nonsense” variants had a period of presentation beyond 36 years(1).
These findings suggest that the specific types of variants can guide us to different strategies for new interventions(1), That is why the screening of BMPR2 in patients with PAH is clinically useful(66). Although all FAP patients with NMD positive BMPR2 variants can potentially develop the disease, only 20% will, which is why it is postulated that the variant-induced haploinsufficiency alone is not enough to cause fAPH in the most patients and that the expression levels of non-"mutated" transcripts can modify the degrees of haploinsufficiency(67). Treatment and prevention measures will depend on the type of variant, in the cases of "nonsense" variants where therapies that increase the expression of BMPR-II from the non-mutated allele may be more effective in preventing or treating the disease(6).
The activation of the NMD pathway results in the mutant transcript’s degradation from a “nonsense” mutation, leaving only the normal BMPR2 protein produced by the non-mutated allele, being quantitatively reduced but qualitatively conserved, which leads to the development of PAH due to “haploinsufficiency.” As for the mutant transcript resistant to the activation of the NMD pathway due to a “missense” mutation, a mutated protein with abnormal function is produced, even affecting the activity of the normal BMPR2 protein produced by the non-mutated allele, where the harmful effect of this Altered protein qualitatively but not quantitatively, results in a "dominant negative" effect that provides greater susceptibility to developing fAPH.
OTHER GENES INVOLVED IN PAH
Pathogenic variants have been described in genes other than BMPR2 that cause disease and are considered less frequent (1-3%) (Seen table 1). The ACVRL1 (ALK1) and ENG genes encode the ALK1 and endoglin receptors, which are type I membrane receptors of the TGF-B superfamily. Heterozygous variants in these genes are directly associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), a Vascular disorder with an autosomal dominant inheritance characterized by the presence of cutaneous telangiectasias and arteriovenous malformations that can develop PAH(7,10,32,46,51,68-73). Patients carrying variants in the ALK1 gene are significantly younger at diagnosis, compared to carriers and non-carriers of variants in BMPR2, which suggests a rapid evolution of the disease in these cases, in addition to presenting a lower response to therapy vasodilator(7). Variants in the ALK1 gene can be present in children with PAH despite not having the clinical picture of THH at the time of identifying the variants. However, they usually develop the disease later(32).
Table 1. Genes associated with FPAH
| Type of PAH, according to MIM | Gen | Location | Phenotype MIM | Encoded protein | Heredity |
| Primary arterial hypertension 1 | BMPR2 | 2q33.1q33.2 | 178600 | BMP receptor type 2 | AD |
| Primary arterial hypertension 2 | SMAD9 | 13q13.3 | 615324 | Sma and Mad related protein 9 | AD |
| Primary arterial hypertension 3 | CAV1 | 7q31.2 | 615343 | Caveolin 1 | AD |
| Primary arterial hypertension 4 | KCNK3 | 2p23.3 | 615344 | Potassium channel member 3, subfamily K | AD |
| Primary arterial hypertension 5, autosomal recessive | PPHR | No mapeado | 265400 | Unidentified | AR |
| Hypertension associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia 1 | ENG | 9q34.1 | 187300 | Endoglin | AD |
| Hypertension Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia 2 | ACVL1 | 12q13.13 | 600376 | Activin receptor 1 A, kinase II-type | AD |
| Type 2 pulmonary veno-occlusive disease | EIF2AK4 | 15q.15.1 | 234810 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor, 2-alpha kinase | AR |
| Not classified | SMAD1 | 4q31.21 | - | Protein related to Sma and Mad 1 | AD |
| Not classified | SMAD5 | 5q31.1 | - | Protein related to Sma and Mad 5 | AD |
| Not classified | BMPR1B | 4q22.3 | - | BMP receptor type 1B | AD |
| Not classified | CBLN2 | 18q22.3 | - | Precerebelline | AD |
Mutations in SMAD 1, SMAD 5, SMAD 9 also members of the TGF-B family are associated with PAH, and its study is requested after the variants in BMPR2, ALK1, and ENG have been analyzed, and no variant has been found(45,47,74).
Another gene involved in PAH is the CAV1 gene that regulates the phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3, and variants in this gene are a rare cause of PAH(10,48). The CAV1 gene encodes a protein called caveolin-1, necessary for the formation of caveola, which is crucial for the binding membrane receptors and the cell signaling cascade’s initiation with the TGF-ß pathway. On the other hand, this pathway controls the growth, differentiation, and apoptosis signaling of various cell types such as pulmonary vascular endothelial cells (ECs) and smooth muscle cells (SMCs(19).
The KCNK3 gene is a member of the two-pore domain potassium channels expressed in the pulmonary arteries’ smooth muscle cells, and variants in the KCNK3 gene are a rare cause of FPAH and IPAH(75).
The CBLN2 gene encodes cerebellin 2, which is expressed in the lung and has been found mainly in explanted lungs of PAH patients and in cultured endothelial cells thereof, which is why it has been suggested that they act in cell proliferation(76). Some studies have revealed that variants in the precerebellum 2 (CBLN2) gene can increase PAH risk by almost twice that of variants in the BMPR2 gene(10).
Other genes recently recognized as possible causes of PAH are the SMAD9 and BMPR1B (ALK6) genes, found mainly in PAH(47,49).
Variants in the EIF2AK4 gene have been identified in multiple families with pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis (PCH) / PAH associated with veno-occlusive disease (PvOD) being homozygous or compound heterozygous variants in the EIF1AK4 gene, corresponding to an autosomal recessive inheritance(77). The protein product of EIF2AK4 belongs to the family of kinases where the alpha subunit of this protein plays a critical role in the induction of angiogenesis, proliferation, and resistance to apoptosis in states of cellular stress. It has also been found that the protein eIF2aK4 interacts with SMAD4, SMAD1, ALK-1, ENG, and TGFBR2, similar to the molecular pathway of the BMPR2 gene(78).
Currently, standard genetic screening methods focus on sequencing the exon coding regions of the BMPR2, ACVL1, ENG, SMAD9, SMAD1, and SMAD5 genes involved in the TGF-ß signaling pathway(19). Genetic studies have allowed a better understanding of the molecular bases of PAH. However, about 30% of HPAH cases and 60-90% of IPAH cases do not have variants in the BMPR2, ALK1, ENG, or genes. SMAD9, which is why it is suggested that there are other genes in the TGF-ß superfamily or different signaling pathways such as BMP / MAPk, p38, Toll-like, and Rho kinase pathway, among others, that may be associated with the development of IPAH and HPAH(79). Ttreatingdiagnosinghe intronic regions, which have not yet been thoroughly studied, are the next step to investigate. The hypothesis is raised that there are also variants at that level(80), where next-generation sequencing allows us to perform an analysis fast and complete of each patient.
GENETIC COUNSELING IN PAH
Genetic counseling is the process by which the patient and their family members are provided with the necessary information on the causes, inheritance,et al. and implications of the genetic disorder they have, by collecting data from the patient's family history, preparing the herdogram and request for genetic-molecular studies, the latter being what allow us to determine the “mutational” state of the members of a family.
To establish the diagnosis of HPAH, it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis in at least two relatives (FPAH) or to identify the germinal variant in an isolated case in the family (IPAH); However, some factors lead to failure to recognize HPAH cases such as incomplete penetrance, an inadequate family history, an incorrect diagnosis of other affected members of the family, or the inability to resort to molecular studies that detect variants such as BMPR2(3).
HPAH (MIM # 178600)(53), is defined as a genetic disorder, with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern (AD), due to the presence of a heterozygous germline mutation mainly in the BMPR2 gene, with incomplete penetrance of 20%(3), variable age of presentation and predominance in women(58). Because it is an AD disorder, when a patient carries a mutation in the BMPR2 gene, they have a 50% risk of transmitting it to their offspring, but because they have a penetrance of 20%, the risk of developing PAH would be 10% (50% x ~ 20%).
Incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity are the greatest difficulties for genetic counseling, because there may be “de novo” cases that are isolated in the family (IPAH) and carry a germ variant, so they should be informed about genetic studies -moleculars available(17) or there could be several family members who are carriers of the variant who have not yet developed the disease and may overlap a positive family history and who at the time of drawing up the herdogram could not be identified(17,81-84).
Genetic-molecular studies should be requested in the cases of FPAH and PAH as part of the study of the disease(1), but we must bear in mind that prior to the genetic study and after its result, genetic counseling must be provided to the patient and their relatives(5), since the results that will be obtained must be explained to the patient, such as the “positive” results, where the causal variants in the analyzed gene are identified; “negative” results, where the causal variant has not been identified in the analyzed gene, results with “variants of uncertain significance” in which the gene variation found has not been previously reported as causing the disease and other similar results associated with disease to be considered pathogenic; and finally the "truly positive" and "truly negative" results in which after the identification of a causal variant of a certain gene in the affected patient, a specific search for the same mutation is carried out in other members of the family, if it is positive, this will indicate that he has inherited the causal gene of the disease and if the result is negative it would indicate that the relative has not inherited the germline variant(83).
We must bear in mind that the performance of these genetic-molecular studies and the results obtained may have psychological implications on the patient and their families, so it must be taken into account that the result will be made known to the affected patients and family members at risk who wish to know it(17), in addition that the management of patients with PAH should always be carried out by a multidisciplinary team with doctors specializing in PAH, geneticists, genetic counselors, psychologists and nurses mainly, for the comprehensive management of the patient and relatives(17,84). Due to the implications that molecular results may have in all patients with genetic disorders, in May 2008 in the USA, the GINA (Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act) was created, which protects members from discrimination at work based on their predisposition genetics(5).
Once the result of the genetic-molecular study has been obtained in the patient, it is important to offer the corresponding follow-up measures, as is the case of carriers of a variant in the BMPR2 gene, who should be requested control echocardiography and counseling corresponding genetics, in this way, if the disease occurs, an early diagnosis can be made and timely therapy provided(43),83-86)this has been recommended in various pulmonary hypertension guidelines . In relation to the above, much is debated about whether the anticipation phenomenon truly exists or is it that possibly asymptomatic family members are alert to the disease and an earlier diagnosis of the disease is made(3).
There are still many gene variants to discover in all forms of PAH, for which we currently have technology such as next-generation sequencing that facilitates the discovery of rare variants in the study of the complete genome of the patient.
CONCLUSION
PAH is a complex heterogeneous disease and the identification of the causal genes in patients affected with FPAH is relevant for genetic counseling and to search for the variant in the rest of their asymptomatic relatives at risk with a predictive purpose. The adequate compilation of the patient's family history data to refer him for the corresponding genetic counseling and to be able to offer him the follow-up and therapeutic options in relation to the molecular results of each patient.
Author’s Contributions: The authors participated in the genesis of the idea, project design, data collection and interpretation, analysis of results and preparation of the manuscript of this research work.
Funding: Self-financed.
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Received: April 16, 2020
Approved: May 31, 2020
Correspondence: Maria del Carmen Castro Mujica
Address: Av. Alfredo Benavides 5440, Santiago de Surco
Telephone: 987597107
Email: mc.castro.mujica@gmail.com
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES