ORIGINAL ARTICLE
REVISTA DE LA FACULTAD DE MEDICINA HUMANA 2021 - Universidad Ricardo Palma10.25176/RFMH.v22i4.4772
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH POSTPARTUM COMPLICATIONS ACCORDING TO A DEMOGRAPHIC AND FAMILY HEALTH SURVEY IN PERU 2019-2020
FACTORES ASOCIADOS A COMPLICACIONES POST PARTO SEGÚN LA ENCUESTA DEMOGRÁFICA Y DE SALUD FAMILIAR EN PERÚ 2019-2020
Kimberley Mauricio
 1,a,
Rubén Huamán
1,a,
Rubén Huamán
 1,a,
Rubén Espinoza
1,a,
Rubén Espinoza
 1,2,b
1,2,b
1Facultad de Medicina Humana, Universidad Ricardo Palma. Lima, Peru.
2Instituto de Investigación en Ciencias Biomédicas (INICIB), Facultad de Medicina Humana,
Universidad Ricardo Palma. Lima, Peru.
aHuman medicine student.
bMaster in Administration and Social Management.
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Postpartum complications are important health problems in Peru, therefore it is necessary to determine their associated factors. Objectives: Determine the factors associated with postpartum complications in Peru during the years 2019 and 2020. Methods: Cross-sectional, analytical study, carried out from the analysis of the Demographic and Family Health Survey (ENDES) 2019-2020, of Peru. The unit of analysis was women between the ages of 12 and 49 residing in Peru in the years 2019-2020. Multivariate analysis was performed using Poisson regression with robust variance. Results: It is evidenced that the age of 20 to 35 years has a prevalence ratio of 1.12 of ending in complications after childbirth (PRa: 1.12, 95% CI: 1.07 to 1.18) compared to women who have 36 years and over. Having complications during childbirth has a 2.75 times higher prevalence of complications after childbirth (APR: 2.75, 95% CI: 2.64 to 2866). Having a degree of primary (RPa: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.84 to 0.96), secondary (RPa: 0.94, 95% CI: 0.89 to 0.98) education decreases the probability of having complications after childbirth compared to women with a higher level of education. and having a single marital status (APR 0.85, 95% CI: 0.76 to 0.94) decreases the probability of having complications after childbirth, compared to cohabitants. Conclution. The prevalence of postpartum complications is regular. The factors associated with postpartum complications are: age, educational level, marital status and complications during childbirth.
Keywords: Puerperal Disorders; Postpartum Period; Postpartum Hemorrhage; Puerperal Infection (Source: MeSH NLM).
RESUMEN
Introducción: Las complicaciones post parto son problemas de salud importante en el Perú, por lo tanto, es necesario determinar sus factores asociados. Objetivos: Determinar los factores asociados a las complicaciones post parto en Perú durante los años 2019 y 2020. Métodos: Estudio transversal, analítico, realizado a partir del análisis de la Encuesta Demográfica y de Salud Familiar (ENDES) 2019-2020, del Perú. La unidad de análisis fueron las mujeres de 12 a 49 años de edad residentes en el Perú en los años 2019-2020. Se realizó el análisis multivariado mediante regresión de Poisson con varianza robusta para hallar las razones de prevalencia crudas y ajustadas con sus respectivos intervalos de confianza al 95%. Resultados: La prevalencia de complicaciones post parto fue 37,7%. Se observó que la edad de 20 a 35 aumentó en 1,12 veces la prevalencia de terminar en complicaciones después del parto en comparación a las mujeres que tienen 36 años a más (RPa: 1,12, IC95%: 1,07 a 1,18). Tener complicaciones durante el parto aumenta en 2,75 veces la prevalencia de complicaciones en el post parto (RPa: 2,75, IC95%: 2,64 a 2866). Tener grado de instrucción primaria (RPa: 0,90, IC95%: 0,84 a 0,96) y secundaria (RPa: 0,94, IC95%: 0,89 a 0,98) disminuyen la prevalencia de tener complicaciones post parto en comparación al grado de instrucción superior; tener estado civil soltera disminuye la prevalencia (RPa 0,85, IC95%: 0,76 a 0,94) de tener complicaciones después del parto, frente al grupo de convivientes. Conclusión. La prevalencia de las complicaciones post parto es regular. Los factores asociados a las complicaciones post parto son: la edad, grado de instrucción, estado civil y complicaciones durante el parto.
Palabras Clave: Trastornos Puerperales; Periodo Posparto; Hemorragia Posparto; Infección Puerperal (Fuente: DeCS BIREME).
INTRODUCTION
The Demographic and Family Health Survey - ENDES is a continuous statistical investigation that is carried out at the national level to obtain updated information about health indicators of the population. This survey is carried out by duly trained personnel, through direct interviews and through home visits to a representative sample of selected households to collect data on maternal and child health, use of health services, chronic non-communicable diseases, nutrition and other important aspects that can be used to follow up, propose health policies and programs. Likewise, this source of information, being freely accessible and having current and true information, can be used by the academic community for future research.
Obstetric complications are a cause of maternal morbidity and mortality worldwide, these can occur during pregnancy, childbirth, or the puerperium. Immediate, mediate and late postpartum complications are important events because it is a stage where physiological and emotional changes occur and the high mortality they produce (1).
In Peru, it was shown that in 2019 and 2020, the stage with the highest frequency of maternal mortality due to direct obstetric causes was the puerperium, with 59.7% and 63.3% respectively, with the leading causes being hemorrhage and sepsis with 55.7%. The highest amount of maternal mortality in 2020 was reported in the departments of Lima Metropolitan, Loreto, Ucayali, Lambayeque, La Libertad, Junín and Cusco (2,3).
Despite the fact that our country managed to reduce maternal mortality by 73%, it is still considered a great threat to pregnant women and constitutes an important public health problem. Therefore, it is essential to identify which complications can occur, and at what stage it can occur (4).
Although obstetric factors are the most studied, sociodemographic factors must also be taken into account, since they have been identified in some studies that are associated with higher maternal mortality, such as the prevalence in young people between 18 and 35 years old, with low socioeconomic status or low level of education, which make it difficult to access information and health services. Therefore, it is important to know the situation in which the Peruvian population finds itself in order to propose health policies that help to reduce morbidity and mortality (5).
The objective of this study is to determine the factors associated with postpartum complications, according to ENDES from 2019 to 2020, and thus contribute with results that help prevent and reduce maternal morbidity and mortality.
METHODS
Type and design
Quantitative, observational, retrospective, cross-sectional and analytical study, based on information from secondary sources contained in ENDES 2019-2020 public database.
Population and Sample
The study population is made up of all women between 12 and 49 years old residing in private homes in Peru in 2019-2020, who have presented complications after childbirth, and who answer the questions of the study variables found in the ENDES. Women who presented complications after 40 days of childbirth, women who answered "Don't know" in the questionnaire and who are residents in collective housing are excluded from the research. Due to the aforementioned criteria, a sample size of 18,115 women aged 12 to 49 years was obtained for the two years. The sample is characterized by being two-stage, probabilistic of a balanced, stratified and independent type, at the departmental level and by urban and rural area, according to the sample design of the Demographic and Family Health Survey(ENDES)2019-2020.
Variables and instruments
The study variables were established from the data present in the ENDES. For the dependent variable: postpartum complications, we included: heavy bleeding (hemorrhage), fainting or loss of consciousness, high fever and chills, breast infection (mastitis), painful urination (dysuria), vaginal discharge, and unintentional discharge of urine (urinary incontinence). For the independent variables, sociodemographic factors were included, which include age, ethnicity, level of education, marital status, type of place of residence, region and wealth index; obstetric factors, including postnatal checkups, cesarean delivery, delivery site, and postpartum complications; and the violence factor, both physical and emotional. Finally, the variables related to the sample design were taken into account, such as the weighting factor V005, conglomerate V001 and stratum V022.
Procedures
For data collection, the official website of the National Institute of Statistics and Informatics (INEI) of Peru was accessed https://www.inei.gob.pe/(6), then the microdata option was entered, consultation by surveys, and the ENDES options for the year 2019 and 2020 with a single period were selected. The files containing the necessary variables of the study were downloaded and a folder with the databases was created for its execution. The ENDES survey uses the survey as a technique and 3 questionnaires as an instrument.
Statistical analysis
For the elaboration and processing of the database, the statistical software SPSS version 26.0 was used. Qualitative variables were analyzed in frequency and contingency tables. To evaluate the association between qualitative or categorical variables, the corrected F statistic was used. As a measure for the evaluation of the risk factors, the crude prevalence ratio (PRc) with its respective confidence interval was used. Finally, the adjusted prevalence ratio (APR) was calculated through a Poisson regression model with robust variance. For the inferential analysis, a confidence level of 95% was used, a statistical significance of p<0.05 and the CSPLAN analysis was elaborated for complex samples according to the sample design and considering the weighting factor, the conglomerate and the stratum.
Ethical aspects
This study is based on the analysis of information extracted from the ENDES database for 2019-2020, which is publicly accessible and the confidentiality of the participants is respected. Likewise, the present study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the "Manuel Huamán Guerrero" Facultad de Medicina Humana- Universidad Ricardo Palma, allowing the continuation of the study.
RESULTS
The initial sample consisted of 19,248 records, which, considering the inclusion and exclusion criteria, a sample size of 18,115 women aged 12 to 49 years was obtained, interviewed in the 2019-2020 Demographic and Family Health Survey.
The prevalence of postpartum complications in 2019-2020 is 37.7% of the total. In 2019, 38.1% of the women aged 12 to 49 presented complications after childbirth. Likewise, in 2020, 37.2% of women presented complications after childbirth. When carrying out the analysis of the geographical distribution of postpartum complications, it was found that the departments San Martín, Cusco, Apurímac, Arequipa, Ayacucho, Huancavelica, Madre de Dios, Pasco, Amazonas and La Libertad present a higher prevalence of 38, 8%-42.5% of postpartum complications, followed by the departments of Moquegua, Junín, Ancash, Huánuco, Lambayeque and Loreto with a prevalence of 35.4%-38.8%. (Figure 1).
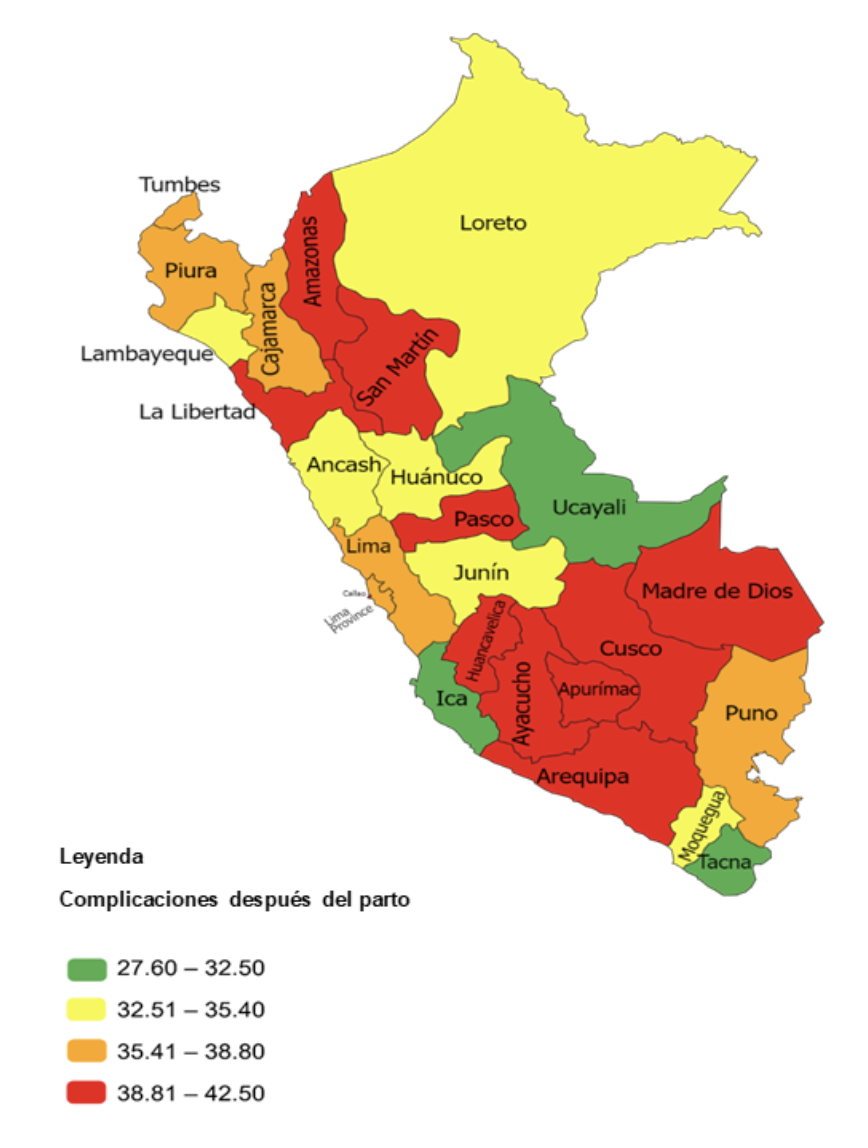
Regarding the general characteristics of the interviewees in the ENDES 2019-2020, the following stands out: In relation to sociodemographic factors, 65.2% of the women are between 20 and 35 years old, 49.7% are from mixed race, 46.3% have a secondary education degree, 59.2% have a marital status of cohabiting, 75.1% live in the urban area, 56.1% are from the Coast region and in terms of the index of wealth 67.7% have little income; regarding obstetric factors, 97.9% had postnatal check-ups, 63.9% did not have a cesarean delivery, 67.8% had the public sector as the place of delivery, and 66.8% had no complications during delivery. ; regarding domestic violence, 67.9% experienced physical and emotional violence during pregnancy.
Furthermore, the coefficient of variation was obtained for each of the variables, where the percentage of said coefficient was less than 15% in most of the variables, this gives us an assurance that the sample obtained is adequate for our research. (Table No. 1).
Tabla 1. General characteristics of women aged 12 to 49, interviewed in the ENDES 2019-2020
|
Characteristic |
n |
% |
Variation Coefficient (%)
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Complications after delivery |
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
No |
11282 |
62,3 |
7,3 |
|
|
Yes |
6832 |
37,7 |
7,4 |
|
|
Age |
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
12-19 |
774 |
4,3 |
8,5 |
|
|
20-35 |
11810 |
65,2 |
7,3 |
|
|
36 or more |
5530 |
30,5 |
7,7 |
|
|
Ethnicity |
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
Black |
2212 |
12,2 |
9,2 |
|
|
White |
1493 |
8,2 |
9,9 |
|
|
Mixed |
9011 |
49,7 |
8,7 |
|
|
Others |
5399 |
29,8 |
7,5 |
|
|
Instruction level |
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
Without education |
233 |
1,3 |
12,9 |
|
|
Elementary |
3013 |
16,6 |
9,6 |
|
|
Secondary |
8388 |
46,3 |
7,6 |
|
|
Superior |
6481 |
35,8 |
9,0 |
|
|
Marital status |
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
Single |
902 |
5,0 |
7,9 |
|
|
Married |
4428 |
24,4 |
7,6 |
|
|
Cohabitant |
10731 |
59,2 |
7,5 |
|
|
widow |
17 |
0,1 |
27,1 |
|
|
Divorced |
24 |
0,1 |
28,2 |
|
|
separated |
2012 |
11,1 |
7,9 |
|
|
Residency type of place
|
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
Urban |
13607 |
75,1 |
8,7 |
|
|
Rural |
4507 |
24,9 |
13,0 |
|
|
Region
|
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
Coast |
10164 |
56,1 |
11,6 |
|
|
Mountain |
4793 |
26,5 |
8,1 |
|
|
Jungle |
3157 |
17,4 |
10,4 |
|
|
Economic earning
|
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
little earning |
12261 |
67,7 |
6,8 |
|
|
Higher earnings |
5853 |
32,3 |
11,8 |
|
|
Postnatal checkups |
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
No |
386 |
2,1 |
22,7 |
|
|
Yes |
17729 |
97,9 |
7,3 |
|
|
Cesarean birth |
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
Yes |
6548 |
36,1 |
8,2
|
|
|
No |
11567 |
63,9 |
7,2 |
|
|
Place of birth |
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
Public sector |
12285 |
67,8 |
6,9 |
|
|
Private sector |
5830 |
32,2 |
9,9 |
|
|
Complications during childbirth |
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
Yes |
6018 |
33,2 |
7,5 |
|
|
No |
12097 |
66,8 |
7,3 |
|
|
Physical and emotional violence |
Total |
18115 |
100,0 |
7,3 |
|
Yes |
12313 |
67,9 |
4,1 |
|
|
No |
5802 |
32,1 |
14,1 |
The bivariate analysis of sociodemographic factors such as age, ethnicity, marital status and wealth index are statistically significantly associated with postpartum complications, with a p-value less than 0.050. There is evidence that being between 20 and 35 years of age (PR: 1.20, 95% CI: 0.99 to 1.21) increases the prevalence of postpartum complications. Regarding the wealth index variable: Low income (PR: 1.06, 95% CI: 1.01 to 1.10); being of black ethnicity (PR: 0.93, 95% CI: 0.87 to 0.99), mix race (PR 0.91, 95% CI 0.87 to 0.95) and marital status: single (PR: 0 .8, 95% CI: 0.79 to 0.95) decreases the probability of having complications after childbirth. Analyzing the level of education: without education (PRc: 1.02, CI95%: 0.87 to 1.21), primary (PRc: 0.97, CI95%: 0.91 to 1.02) and secondary (PRc : 1.01, 95% CI: 0.97 to 1.06), type of place of residence: urban (PRc: 0.99, 95% CI: 0.95 to 1.03) and region: Coast (PRc: 1 .01, 95% CI: 0.96 to 1.07) and mountain (PRc: 1.04, 95% CI: 0.98 to 1.11) no statistical association was found because the confidence interval of the PR contains the unit. (Table No. 2).
Table No. 2 Bivariate analysis of sociodemographic factors associated with postpartum complications in women aged 12 to 49 years, according to ENDES 2019-2020.
|
Sociodemographic factors |
|
Complications after childbirth |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
No |
RPc |
CI95% |
P value |
|||||
|
Abs |
% |
Abs |
% |
||||||
|
Age |
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
11282 |
100,0 |
|
0,000*
|
||
|
12-19 |
283 |
4,1 |
491 |
4,4 |
1,10 |
0,99-1,21 |
|||
|
20-35 |
4712 |
69,0 |
7099 |
62,9 |
1,20 |
1,14-1,25 |
|||
|
36 or more |
1838 |
26,9 |
3692 |
32,7 |
Ref. |
||||
|
Ethnicity |
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
11282 |
100,0 |
|
0,000*
|
||
|
Black |
825 |
12,1 |
1387 |
12,3 |
0,93 |
0,87-0,99 |
|||
|
White |
578 |
8,5 |
914 |
8,1 |
0,97 |
0,90-1,04 |
|||
|
Mixed |
3277 |
48,0 |
5734 |
50,8 |
0,91 |
0,87-0,95 |
|||
|
Others |
2153 |
31,5 |
3246 |
28,8 |
Ref. |
||||
|
Instruction level
|
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
11282 |
100,0 |
|
0,232
|
||
|
Without education |
90 |
1,3 |
143 |
1,3 |
1,02 |
0,87-1,21 |
|||
|
Elementary |
1098 |
16,1 |
1915 |
17,0 |
0,97 |
0,91-1,02 |
|||
|
Secondary |
3210 |
47,0 |
5177 |
45,9 |
1,01 |
0,97-1,06 |
|||
|
Superior |
2434 |
35,6 |
4047 |
35,9 |
Ref. |
||||
|
Marital status |
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
11282 |
100,0 |
|
0,025*
|
||
|
Single |
302 |
4,4 |
600 |
5,3 |
0,87 |
0,79-0,95 |
|||
|
Married |
1642 |
24,0 |
2787 |
24,7 |
0,96 |
0,9-1,008 |
|||
|
Widow |
8 |
0,1 |
9 |
0,1 |
1,22 |
0,73-2,02 |
|||
|
Divorced |
6 |
0,1 |
18 |
0,2 |
0,65 |
0,32-1,30 |
|||
|
Separated |
746 |
10,9 |
1266 |
11,2 |
0,96 |
0,90-1,02 |
|||
|
Cohabitant |
4129 |
60,4 |
6602 |
58,5 |
Ref. |
||||
|
Residency type of place |
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
11282 |
100,0 |
|
0,738
|
||
|
Urban |
5123 |
75,0 |
8485 |
75,2 |
0,99 |
0,95-1,03 |
|||
|
Rural |
1710 |
25,0 |
2798 |
24,8 |
Ref. |
||||
|
Region
|
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
11282 |
100,0 |
|
0,189
|
||
|
Coast |
3813 |
55,8 |
6352 |
56,3 |
1,01 |
0,96-1,07 |
|||
|
Mountain |
1854 |
27,1 |
2939 |
26,1 |
1,04 |
0,98-1,11 |
|||
|
Jungle |
1166 |
17,1 |
1991 |
17,6 |
Ref. |
||||
|
Economic earning |
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
1282 |
00,0 |
|
0,005*
|
||
|
little earning |
4710 |
68,9 |
7551 |
66,9 |
1,06 |
1,01-1,10 |
|||
|
Higher earnings |
2122 |
31,1 |
3731 |
33,1 |
Ref. |
||||
|
*Significant PRc: crude prevalence ratio CI95%: confidence interval at 95% Ref: reference category |
|||||||||
Obstetric factors such as postnatal checkups, place of delivery, complications during childbirth and violence factor, both physical and emotional, are associated in a statistically significant way with postpartum complications, with a p-value less than 0.050. It is evident that the following factors increase the prevalence of postpartum complications: Failure to present postnatal check-ups (PRc: 1.16, 95% CI: 1.03 to 1.30), place of delivery: public sector (PRc: 1.06 , 95% CI: 1.02 to 1.11) and having developed complications during childbirth. (PRc: 2.79, CI95%: 2.69 to 2.89), physical and emotional violence (PRc: 1.05, CI95%: 1.01 to 1.09). Regarding having a cesarean delivery (PRc: 0.96, 95% CI: 0.92 to 0.99), the probability of having complications after delivery decreases. (Table No. 3).
Table No. 3. Bivariate analysis of obstetric factors and the violence factor associated with postpartum complications in women aged 12 to 49 years, according to ENDES 2019-2020.
|
Obstetric factors and violence factor |
Complications after childbirth |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
No |
RPc |
CI95% |
P vale |
||||
|
Abs |
% |
Abs |
% |
|||||
|
Postnatal checkups |
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
11282 |
100.0 |
|
0,001*
|
|
|
No |
169 |
2,5 |
217 |
1,9 |
1,16 |
1,03-1,30 |
||
|
Yes |
6663 |
97,5 |
11065 |
98,1 |
Ref. |
|||
|
Cesarean birth |
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
11282 |
100,0 |
|
0,029*
|
|
|
Yes |
2407 |
35,2 |
4141 |
36,7 |
0,96 |
0,92-0,99 |
||
|
No |
4426 |
64,8 |
7141 |
63,3 |
Ref. |
|||
|
Place of birth |
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
11282 |
100,0 |
|
0,003*
|
|
|
Public sector |
4727 |
69,2 |
7558 |
67,0 |
1,06 |
1,02-1,11 |
||
|
Private sector |
2106 |
30,8 |
3724 |
33,0 |
Ref. |
|||
|
Complications during childbirth |
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
11282 |
100,0 |
|
0,000*
|
|
|
Yes |
3972 |
58,1 |
2045 |
18,1 |
2,79 |
2,69-2,89 |
||
|
No |
2860 |
41,9 |
9237 |
81,9 |
Ref. |
|||
|
Violence physical and emotional |
Total |
6832 |
100,0 |
11282 |
100,0 |
|
0,009*
|
|
|
Yes |
4720 |
69,1 |
7593 |
67,3 |
1,05 |
1,01-1,09 |
||
|
No |
2112 |
30,9 |
3689 |
32,7 |
Ref. |
|||
The results of the multivariate analysis show that the age of 20 to 35 years has a prevalence ratio of 1.12 of ending in complications after childbirth (PRa: 1.12, 95% CI: 1.07 to 1.18). Having complications during childbirth is 2.75 times more prevalent than complications after childbirth (PRa: 2.75, CI95%: 2.64 to 2866). Have a primary education level (RPa: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.84 to 0.96), secondary education (RPa: 0.94, 95% CI: 0.89 to 0.98) and have a single marital status (RPa 0.852, 95% CI: 0.76 to 0.94) decrease the probability of having complications after childbirth. (Table No. 4).
Table No. 4. Multivariate analysis of the factors associated with postpartum complications in women aged 12 to 49 years, according to ENDES 2019-2020.
|
Associated factors |
Complications after childbirth |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
RPa |
CI95% |
p value |
||||
|
Sociodemographic |
||||||
|
Age |
12-19 |
1,04 |
0,93-1,16 |
0,443 |
||
|
20-35 |
1,12 |
1,07-1,18 |
0,000* |
|||
|
36 or more |
Ref. |
|||||
|
Ethnicity
|
Black |
0,97 |
0,91-1,03 |
0,429 |
||
|
White |
1,01 |
0,94-1,08 |
0,686 |
|||
|
Others |
0,95 |
0,91-1,00 |
0,082 |
|||
|
Mixed |
Ref. |
|||||
|
Instruction level |
Without education |
0,93 |
0,79-1,08 |
0,354 |
||
|
Elementary |
0,90 |
0,84-0,96 |
0,004* |
|||
|
Secundary |
0,94 |
0,89-0,98 |
0,015* |
|||
|
Superior |
Ref. |
|||||
|
Marital status
|
Single |
0,85 |
0,76-0,94 |
0,003* |
||
|
Married |
0,96 |
0,91-1,01 |
0,128 |
|||
|
Widow |
1,28 |
0,784-2,091 |
0,324 |
|||
|
Divorced |
0,64 |
0,29-1,36 |
0,249 |
|||
|
Separated |
0,98 |
0,91-1,05 |
0,595 |
|||
|
Cohabitant |
Ref. |
|||||
|
Residency type of place |
Urban |
1,00 |
0,94-1,05 |
0,997 |
||
|
Rural |
Ref. |
|||||
|
Region |
Coast |
0,98 |
0,92-1,05 |
0,683 |
||
|
Mountain |
0,96 |
0,90-1,02 |
0,273 |
|||
|
Jungle |
Ref. |
|||||
|
Economic earning
|
Little earning |
1,02 |
0,97-1,08 |
0,258 |
||
|
Higher earnings |
Ref. |
|||||
|
Associated factors |
|
Complications after childbirth |
||||
|
RPa |
CI95% |
P value |
||||
|
Obstetricians |
||||||
|
postnatal checkups |
No |
1,08 |
0,98-1,19 |
0,120 |
||
|
Yes |
Ref. |
|||||
|
Cesarean birth |
Yes |
1,00 |
0,96-1,05 |
0,727 |
||
|
No |
Ref. |
|||||
|
Place of birth |
Public sector |
1,02 |
0,97-1,07 |
0,356 |
||
|
Private sector |
Ref. |
|
||||
|
Complications during the delivery |
Yes |
2,75 |
2,64-2866 |
0,000* |
||
|
No |
Ref. |
|||||
|
Violence |
||||||
|
Physical and emotional violence |
Yes |
1,02 |
0,98-1,07 |
0,215 |
||
|
No |
Ref. |
|||||
|
*Significant Pa: adjusted prevalence ratio CI95%: confidence interval at 95% Ref: reference category |
||||||
DISCUSION
In the present manuscript, regarding the prevalence of postpartum complications in women aged 12 to 49 years, according to ENDES 2019 and 2020, it is evident that of the total sample (18,115), 37.70% did present complications after childbirth, and 62.30% did not present them. At national level, these figures are similar to those obtained by Méndez and Morales according to ENDES 2017 to 2019, where the prevalence of postpartum maternal obstetric complications in the total sample was 28.7% (7). Pereira, in his research carried out at the Hospital Maria Auxiliadora Hospital, showed a prevalence of 33.3% of postpartum complications and Vargas found a prevalence of postpartum complications of 13.8% at the Hospital Nacional Arzobispo Loayza (8,9).
Regarding international studies, Villarreal, at the Historic Center Health Center in Quito, observed that 12% of women presented some complication during the puerperium (10). Likewise, in the study by Páez and Romero in Bogotá-Colombia, it was shown that 6.3% of the pregnant women attended in the high complexity hospital presented puerperal complications (11).
The prevalence obtained in our study together with the obtained in other national studies, have a higher percentage of puerperal complications unlike international studies, this could be due to the fact that in our country no greater measures and health policies have been taken for adequate care during the stage of pregnancy, through an adequate diagnosis, stabilization and timely referral to an establishment with greater resolution capacity (12).
Age in the range of 20 to 35 years old is a sociodemographic factor associated with postpartum complications (p<0.05). These results are similar to the study carried out at the national level by Vargas, who reported that the age group with the highest prevalence was between 18 and 35 years with 78.9% (9). Zegarra, in his study, observes that the women who had the highest frequency of puerperal complications were in the group of 25 to 29 years, representing 25.1% of the population, but analyzing the 8 age groups used in his study, it is evident that 3 age groups that cover the ages between 20 to 34 years are the ones with the highest frequency of puerperal complications (13).
At the international level, Villarreal in his study, observed that 37% of women aged between 20 and 24 years had a higher percentage of complications after childbirth (10). This could be explained due to the lack of information of the young women about the warning signs and postpartum care (13).
Our results differ from studies,like Paéz and Romero's study for example, where the group older than 35 years was the most frequent with postpartum complications with 9.5% (11). Otherwise, Martínez and Brizuela, obtained a prevalence of 32% of complications in the puerperium in the age group between 15 and 19 years (14). Furthermore, Sikder et al, showed in their multivariate analysis that women under 18 years of age (relative risk ratio [RRR] 1.26; 95% CI: 1.14-1.39) and over 35 years of age (RRR 1.23 95% CI: 1.09-1.38), significantly increased the risk of having obstetric complications during the puerperium(15).
The education level is a sociodemographic factor associated with complications after childbirth. Having Primary (PRa: 0.90, CI95%: 0.84 to 0.96) and Complete Secondary (PRa: 0.94, CI95%: 0.89 to 0.98) decreases the probability of having complications after childbirth . This differs from Naula et al, who carried out their study at the Vicente Corral Moscoso hospital, in Cuenca-Ecuador, and observed that the complete secondary level predominated in the population of puerperal women who presented complications (47.2%), being these among the most frequent characteristics of your study(16).
At the national level, Delgado observed that postpartum women who had complications were characterized by having completed secondary education in 29.89% (17). Méndez and Morales determined the education level of women in the puerperium; mothers with no studies or with primary education (PR= 0.84; 95% CI= 0.78 – 0.90) and women with secondary education (PR= 0.93; 95% CI= 0.89 – 0.98 ) are less likely to present complications during the puerperium (7). These data are compatible with the results of our study. Quispe showed that the puerperal women with the lowest percentage of bleeding complications had only primary level, representing 1.7% of the total of the educational level variable (18). Our results could be due to the fact that the group of women with primary and secondary level surveyed did not understand well the interviewer's question about the symptoms of complications, they may have underestimated the intensity of the symptoms and did not consider them as a complication.
Marital status is an associated sociodemographic factor (p value <0.05). Being single (OR: 0.87, 95% CI: 0.79 to 0.95) decreases the probability of having complications after childbirth. This result coincides with international studies by Páez and Romero, where they showed that women with single marital status were the ones who presented the lowest percentage of puerperal complications with 23.8%(11). Unlike Villarreal, the group of women with single marital status obtained 37%, being the group with the highest percentage of complications after childbirth (10). Likewise, Martinez and Brizuela in their study, observed that women with complications during the puerperium with single marital status reached 37.3%, being the second highest group within the marital status variable (14). Naula et al, report that women with postpartum complications with married marital status and free union predominated with 42.5% and 43% respectively (10). Our result could be explained by the fact that many of the single mothers in Peru have family support in terms of education, food, maintenance and protection, so they can go to health centers for postnatal medical check-ups(19).
Regarding complications during childbirth, an association was found with complications after childbirth (p value <0.05). These include prolonged labor, excessive bleeding, fever with vaginal bleeding, seizures, and others. The Vargas study shows that 61% of patients with postpartum hemorrhage had a prolonged delivery. Likewise, it was recorded that 95.6% of women with postpartum complications presented excessive bleeding during childbirth(9).
Huvin concludes that having had complications during childbirth is significantly associated with puerperal complications in Peruvian women, this being one of the main risk factors in their study, since they have a 2.25-fold probability of presenting complications during the puerperium. (p= 0.001) (20). Montenegro and Arango analyzed the perinatal variables in their study, where significance was only obtained for the presence of complications during childbirth, with an OR of 6.98 and a value of p=0.000 (21). This is due to the fact that the main puerperal pathologies that cause the highest mortality occur just after childbirth, in the immediate puerperium. Therefore, if complications occur during labor, they could influence the development of complications during the puerperium.
The main limitation of this research is that there was no access to hospital centers, so we worked with a source of secondary data, generating a limitation when choosing the study variables, such as postpartum complications, for this reason we did not could add more variables of importance. Furthermore, as it was a retrospective cross-sectional study, the association could be established, but not the causality between the variables studied. It is recommended to carry out prospective studies that identify other associated factors, this will be very helpful to identify patients with a high risk and thus intervene effectively to reduce the epidemiological impact of these complications on maternal morbidity and mortality both nationally and internationally.
CONCLUSIÓN
In conclusion, the factors associated with postpartum complications, according to the ENDES, Peru - 2019-2020, are age and complications during childbirth.
The level of education and marital status were found to be protective factors.
Authorship contributions: The authors participated in the design, data
collection, analysis of results, and approval of the final version of the article..
Funding sources: Self-financed.
Conflicts of interest: he authors declare that they have no conflicts of
interest.
Received: February 19th 2022
Approved: May 24th 2022
Correspondence: imberley Lissette Mauricio Fernández .
Address: r. Combate de Angamos 745. Residencial Jardines de Surco A-401.
Santiago de Surco.
Telephone number: +51 950669243
E-mail: kimberleylissette@gmail.com
Article published by the Journal of the faculty of Human Medicine of the Ricardo Palma University. It is an open access article, distributed under the terms of the Creatvie Commons license: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International, CC BY 4.0(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/), that allows non-commercial use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original work is duly cited. For commercial use, please contact revista.medicina@urp.edu.pe.
REFERENCES
