ARTÍCULO DE REVISIÓN
REVISTA DE LA FACULTAD DE MEDICINA HUMANA 2022 - Universidad Ricardo Palma10.25176/RFMH.v22i2.4790
INTELLIGENCE IN HEALTH. A CRITICAL ANALYSIS STRATEGY FOR DECISION-MAKING IN THE HEALTH AREA
INTELIGENCIA EN SALUD: UNA ESTRATÉGIA DE ANÁLISIS CRÍTICO PARA LA TOMA DE DECISIONES EN EL SECTOR DE SALUD
Augusto Flavio Figueroa Uribe1,2,a, Julia Hernández Ramírez3,4,5, Jorge Omar Flores del Razo 6,a
1 Maestro en Administración de la Seguridad con Especialización en Inteligencia para la
Seguridad Nacional
2 Subdirector Médico Hospital Pediátrico Peralvillo SSCDMX, México
3 Maestra en Educación con Especialidad en Innovación Educativa
4 Enfermera Pediatra y Administradora de los Servicios de Enfermería
5 Coordinadora de Enseñanza de Enfermería Hospital Pediátrico Peralvillo SSCDMX
6 Asistente de la Dirección Hospital Pediátrico Peralvillo SSCDMX, México
a Urgenciólogo Pediatra/Toxicólogo
ABSTRACT
The last year and a half, it was shown that the lack of use of data and information of origin in the health sector, produced one of the greatest catastrophes that it has experienced mankind in the last 100 years. The aforementioned is due to a failure of vision, which unfortunately is seen as a problem not only of national security but also of human security. Intelligence is the discipline that carries out the planning, collection, analysis, and generation of products for the decision-making of the leaders of a country, sector, organization, or society. This can be used very well in the health sector, applying the intelligence cycle model used in the security or financial field. That is, generating products from the analysis of raw information, lines of action, strategies, and prospective scenarios that guide the decision-maker to carry out health policies that comply with the human security strategies recommended by the United Nations (UN) for sustainable development.
Keywords: Intelligence in Health; Human Security; Disasters; Risk Analysis; Epidemiology; Data Mining; Intelligence Cycle. (Source : MeSH - NLM).
RESUMEN
En el último año y medio, se demostró que la falta de utilización de datos e información de origen en el sector salud produjo una de las mayores catástrofes que ha vivido la humanidad en los últimos 100 años. Inteligencia es la disciplina que realiza la planeación, recolección, análisis y generación de productos para la toma de decisiones de los líderes de un país, sector, organización o sociedad. Se puede utilizar muy bien en el sector salud, aplicando el modelo del ciclo de inteligencia utilizado en el ámbito de seguridad o financiero. Es decir, generando productos del análisis de la información bruta, líneas de acción, estrategias y escenarios prospectivos que orienten al tomador de decisiones a realizar políticas en salud que cumplan con las estrategias de seguridad humana que recomienda la Organización de Naciones Unidas (ONU) para un desarrollo sustentable.
Palabras Clave: Inteligencia en Salud; Seguridad Humana; Análisis de Riesgos; Epidemiologia; Minería de datos; Ciclo de inteligencia. (Fuente: DeCS BIREME).
INTRODUCTION
For a year and a half, one of the greatest disturbing phenomena considered in Comprehensive Disaster
Management has been and continues to plague the world, causing major crises in various sectors of human
development(1) such as health, economy, security, development, political,
social and educational. It is a multidimensional security problem since it affects the stability and
permanence not only of the poorest or weakest states but also of the hegemonic states; And if we value
the losses in all contexts, they were the biggest losers, and the safest thing to come out of this
pandemic will be another world with other balances of power that we will see in the future.(2)
The present world is for a large part of society an insecure place, full of threats that come
from all kinds of places, if they already existed, now they are more visible. Crises of all kinds
prolong violent conflicts, natural and man-made disasters, existing poverty, health problems such as
epidemics and economic recessions that cause hardship and destabilize the balance, the goals of peace,
stability, and sustainable development. These crises of complex characteristics by nature mean a great
variety of forms of human insecurity. When these forms are abandoned, insecurity increases exponentially
and affects all aspects of people's lives, from the family, communities, states, and across borders
between countries, becoming a multidimensional, hemispheric, or, in this case, international problem,
causing a serious imbalance in what is now called human security.
But what is human security? According to resolution 66/290 of the UN General Assembly, "human
security is an approach that helps the Member States to identify and overcome the generalized and
intersectoral difficulties that affect the survival, the means of subsistence and the dignity of its
citizens”. The resolution calls for: “people-centered, comprehensive, context-specific and
prevention-oriented responses that strengthen the protection and empowerment of all”.(3) The concept of Human Security is made up of two main axes: development and
hard security. These, in turn, have their own intervention axes: (4)
Development Axis
1.- Health development
2.- Environmental development and protection (includes natural disasters)
3.- Economic development
4.- Food development
Hard Security Axis
1.- Political security
2.- Personal security
3.- Community(4)
Being human security one of the axes that the UN has promoted, in most of its members we see
that security is more than the classic concept towards the forces of order and the armed forces against
insecurity by criminal groups, the concept is broader, saying that security is not only that but depends
on multiple factors(5). This means that if the authorities intervene in
security and not in development and vice versa, there will always be unequal growth and surely the
expected result of the concept of human security is more than just security from harm caused by violence
and that entails the development of other axes so that the human really reaches that state of integral
security that will make him fully develop as an individual and as a society(6).
As we have seen, one of the axes of development is the health sector, as an important part of
human security and which is currently part of various development indicators worldwide, including the
multidimensional indicatorofextremepovertyoftheEconomic CommissionforLatinAmericaandtheCaribbean
(ECLAC)(7).
If a community does not have health, it will not only have repercussions in this very sensitive
area of the humanbeing,butitwillalsohaveconsequences extendedtoothersectors,suchasdevelopment,
economic,political,andsocial.Therefore,decision-making by the health leaders of each country, at their
levelofresponsibility,generatespublicpolicies, strategies,andinterventionsforadequate development of the
health sector that depends on an accurateanalysisofalltheinformationthatis generated. in this health
sector; that merits that these data converted into information be collected, analyzed, valued, to result
in various strategies that the leader could take.
The aforementioned can be applied from the operational in an emergency room or to the level of a
health leader of your nation. For this, the teachings and examples of the discipline of strategic,
tactical, and/or operational intelligence in the security area have been taken and applied at a
business, economic level and by various organizations to be able to make the best decisions in the face
of an accumulation of information and with this the making of complex decisions. For this, in the health
area, there is the so-called Intelligence in Health that we will address in this article explaining from
its definition, how to use it to come up with a product that helps the leader to make the decision of
the most appropriate strategy for development, answer to a crisis or prevent a future problem.
(3,5,6,8)
DEFINITION AND TYPE OF INTELLIGENCE INFORMATION
The handling of any type of information inevitably causes the classification of all its forms or
modalities. This activity is used when we handle a discipline such as intelligence, whose appearance in
the public domain of society is technically recent, although its practice already has several
centuries(9).
There are different definitions of intelligence depending on the country and/or organization to
which we refer since its objectives and goals will define the scope and dimensions of the intelligence
activity. One of the first to define intelligence activity was Sherman Kent (10) in the field of national security where he identified three important
components:
a) The product derived from the management and transformation of information and knowledge
b) The organization that carries out this activity
c) The processes through which it is carried out(10,11)
In Mexico, according to article 29 of the National Security Law, intelligence is defined as:
"the knowledge obtained from the collection, processing, dissemination, and exploitation of the
information, for decision-making in matters of national security"(12-13).
The generation of intelligence products is aimed at and focused on knowledge in an analytical,
critical, and in-depth way the phenomena that could be threats and risks to national, internal, and
public security, with the consequent generation of strategies and analysis of the probability of impact
and occurrence, as well as all the variables and the relationship of their cause among
themselves(15).
This we can define as intelligence the process by which a product is obtained that is the result
of submitting data, information, and knowledge to an intellectual process of analysis that will turn
them into reports, either with lines of action or strategies to satisfy the needs of the decision-maker,
politician, military, police, economic, financial, health, business, etc(11).
Previously, Intelligence was related more to security activities of all kinds, but currently,
because it is an adequate process of obtaining analysis, analysis, and generation of products for
decision making; Its use has spread to various areas such as the financial, economic, health sector,
etc. The discipline of intelligence is classified according to the role it plays in decision-making
processes, by the field from which it is generated, or by its level of analysis and strategic
content(15).
| TYPE | AREA | OBJECTIVE | GENERATING INSTANCE | DIRECTED |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic intelligence |
It refers to the prevention and deterrence of risks and threats from a multidimensional vision that in the short, medium and long term allows directing activities and public policies in the discipline that is developed (security, financial, health, etc.) around two major aspects:
|
Generate intelligence products for high-level decision-making activities related to the development of strategies, policies and actions to prevent, deter, contain and neutralize risks and threats to national security from a structural perspective and with a short-term objective. , medium and long term.(14) | National Intelligence Center (CNI), Military or Naval Intelligence, etc. | High-level officials (Executive, Judicial Power, etc.) Senior military commanders |
| Operational intelligence | It consists of intelligence products directly related to carrying out actions to contain and neutralize risks and threats in the operational field. It is generally subservient to the product of tactical intelligence. (17,18) | Give enough information to discern the immediate lines of intervention on the threat or risk. | Police, naval, military or organizational intelligence apparatus. | Lower management and line personnel who carry out operational interventions. |
| Tactical Intelligence | It is the intelligence product that is elaborated to help the realization and design of punctual strategies that allow reaching an objective of small scope and subordinated to the objectives of strategic intelligence. In the field of organizations of a financial, health or business nature, it has a more operational nature, by carrying out specific actions to achieve an immediate result. For example, the measures to be taken to contain an epidemic, etc. | Generating intelligence products related to the identification, monitoring, and understanding of the visible and invisible consequences of risks and threats within the organization. | Police, naval, military or organizational intelligence apparatus. | Middle or lower management and line personnel who carry out operational interventions. |
| Prospective Intelligence | Its result is from the lines of action and/or Strategic Intelligence(16-18). | It is the intelligence product that tries to anticipate the evolution of one or several phenomena, and the probabilities of the actions or inactions of actors that participate in different types of scenarios, from favorable and futuristic to catastrophic, to determine the preventive actions to be carried out. (18,19) | Strategic intelligence devices. | High-level government officials. CEOs of companies, heads of ministries, and secretaries of state. Directors of government organizations. |
| Military intelligence | Information generated for the realization of strategies for the execution of operational-tactical operations in the military and naval field. | Determine the lines of action for military action and intervention at a strategic, tactical and operational level. | Military and naval intelligence apparatus. | Senior military and naval commanders. Decision-making personnel involved in security cabinets. |
| Scientific intelligence | Es el producto de inteligencia de la que se obtiene y procesa la información científica y tecnológica en los ámbitos civiles como militares, que puede afectar la seguridad de un estado o la competitividad de una empresa. | Implement strategies to obtain updated scientific information that allows the development of competitive technology. | Government strategic intelligence units and business intelligence units. | High-level government decision-makers and company CEOs. |
| Financial intelligence | The integration of economic and financial matters with security and development aspects has generated a need for intelligence on them.(20) | Analyze internal and external economic information in all areas to make estimates of prospective economic scenarios and their repercussions in the field of security and development according to the axes of human security. | Government and business financial intelligence units. | High-level decision-makers, company CEOs. |
| Epidemiological or medical intelligence | It is known as MDINT is that which is obtained from the information and analysis of epidemiological and environmental elements to determine the biological, chemical, and nuclear risks of a given place.(20,21) | Analyze information on epidemiological factors to design prevention and mitigation strategies for phenomena of biological, chemical, or nuclear origin. It could correspond to a level of operational and tactical intelligence in the health sector. | Medical intelligence units. | Middle or lower management and line personnel carry out operational interventions. |
| Health intelligence | It refers to the intelligence product generated for the prevention and dissuasion of risks and threats from a multidimensional vision in the short, medium, and long term; It allows to guide activities and public policies in the area of health.((19-20) | Generate intelligence products for the decision-making activities of high-level decision-makers related to the development of strategies, policies, and actions that allow preventing, deterring, containing, and neutralizing risks and threats in the health sector and that could become a health problem. national or internal security, from a structural and conjunctural vision with a short, medium and long term objective. | Advisory bodies and intelligence units of the ministries and secretaries of health. | High-level officials and directors of health units. |
| CEO: Chief Executive Officer (top executive of the company). | ||||
DEFINITION OF HEALTH INTELLIGENCE
Health intelligence is defined as "the ability to solve health problems by obtaining, analyzing and
generating strategies and lines of action that articulate human, technological and research resources,
through monitoring, evaluation and analysis of the health situation, using the various sources of
information on risks and damages, not only from the institution involved but from sources external to
it, all of which has as an expression the adequate generation of policies and the development of
evidence-based management, aimed at achieving the well-being of the population in terms of
health"(20).
The WHO, for its part, defines it as “the actions in Health that work to expand the use of
information for health, including data management, forecasting and the establishment of scenarios, using
cutting-edge information technology. Health intelligence is also responsible for coordinating the
monitoring of the health-related SDGs (UN Sustainable Development Goals). Thus, it gathers and provides
strategic information and intelligence to develop and implement evidence-based policies and sound
decisions on public health issues at all levels.(21).
OBJECTIVES OF INTELLIGENCE IN HEALTH
The generation of Intelligence Information in Health has three main objectives:
1. With the analysis of information and the generation of strategies and lines of action, to
help make complex decisions in these areas.
2. It helps manage, develop and evaluate programs and interventions based on their effectiveness and
efficiency.
3. Have reliable information for consultation by the various institutional actors (22,23).
WHY INTELLIGENCE IN HEALTH WORKS
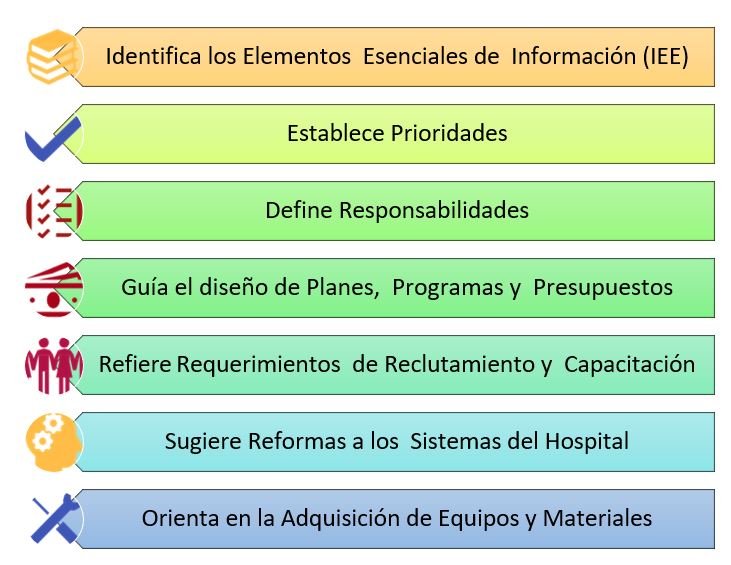
The role of intelligence in health is as broad as any of its counterparts in other areas. Probably, together with strategic intelligence, it is one of the most complexes that exists due to the type and amount of information it handles. In the following image, we summarize the functions of this (22-24).
INTELLIGENCE CYCLE IN HEALTH
The application of a methodology or the full identification of the set of problems known today by the
name "Intelligence Cycle" already existed outlined in other perspectives of knowledge such as the
scientific method. Which is a structured methodology for research, analysis, and results of a previously
stated hypothesis; Its analog today and with some minor differences in the intelligence cycle, which is
mainly adapted to the analysis of information to help the leader make decisions according to the results
of this research(24).
The intelligence cycle has practically standardized steps; but based on the policies and
research processes of each state, organization, or sector used, it may differ in some, mainly adding or
decreasing. The process described below is based on the intelligence cycle used by the National
Intelligence Center (CNI) of Mexico and adapted for Health Intelligence (25).
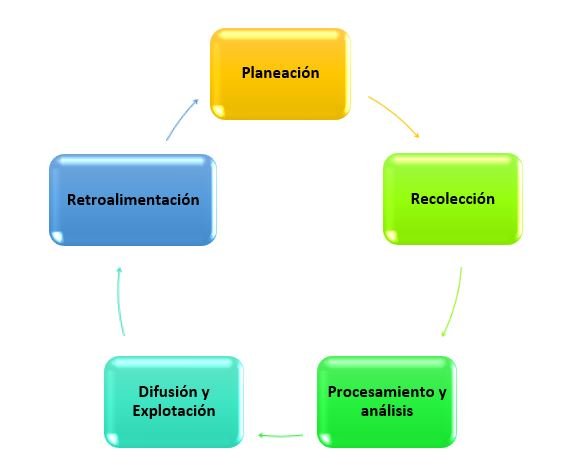
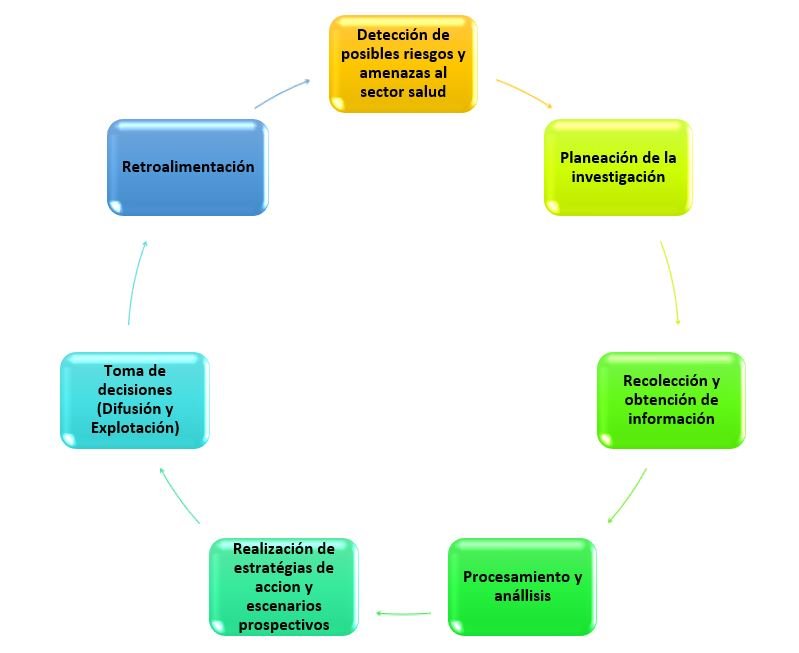
(*)Health Intelligence Cycle suggested by the authors based on the security intelligence (26)cycle and the steps to follow to obtain health products (26)
DETECTION OF POSSIBLE RISKS AND THREATS TO THE HEALTH SECTOR
The timely detection of threats and risks that may affect the health sector requires extraordinary
sensitivity to be able to pertinently detect data and information that can become in a problem or even,
depending on the origin and magnitude, in a disturbing agent causing a disaster, for example, an
epidemic(27).
There are different sources of information that generate data in real-time that can alert us
that something is going wrong or that something wrong is coming out of the usual behavior in a place or
area of the country. The most important sources of information are(28):
- The health surveillance observatories of various public and private institutions (epidemiological, toxicological, health care, etc.).
- The endemic channels of various diseases give us the behavior mainly of infectious and chronic diseases that are out of their normal behavior.
- Mortality, prevalence, and incidence rates that are out of the expected for the indicated moment(29).
- The rate of sentinel units in the country.
- Indicators at yellow or red traffic lights at any given time.
- Information was given by public information media.
These would be the most important sources of alerts, but there may be others that can alert us. Here, the most important thing is that there is enough sensitivity, knowledge, and openness to be able to decide that this could be a problem of such a degree that it could affect the health sector and become an internal or national security problem for the state. These errors minimize notices that in no less Sometimes they are “very subtle”, they have truly materialized into problems, if not even into disasters that have affected the stability of the state, becoming a real problem of national security. examples in the history of Black Swan-type phenomena(1). There are many(34). For this reason, adequate sensitivity is required to be able to detect possible problems that deserve to be investigated in order to make preventive and mitigating decisions, without falling into paranoia and this leads to useless work and waste of resources without reason(31).
PLANNING OF THE INVESTIGATION
Once the reason for the investigation has been found, in this phase, the person in charge carries out
the planning from the formation of work teams with their responsibilities, the areas of investigation,
the objectives and goals to be pursued, the sources and type of information that is will use.
It is important to define the profiles of the members of the work teams since these will be
important for the proper collection of information and its subsequent analysis by the team dedicated to
this.
Here the delivery times with schedules of activities will also be specified, as well as the
possible expected results(33).
COLLECTION AND OBTAINING OF INFORMATION
It consists of obtaining and gathering raw information, that is, the basis of intelligence to be
analyzed by a specialist in the area. The development of a health intelligence product occurs because a
specific requirement appears, either from the potential users or from the health intelligence service
itself, which has found possible risks or threats that could affect it(34).
The most important sources that can be used for this purpose are:(35)
- HUMINT Human Sources. It is made from information collected or supplied directly by people. For example, those obtained from verbal autopsies during an epidemiological fence.(34).
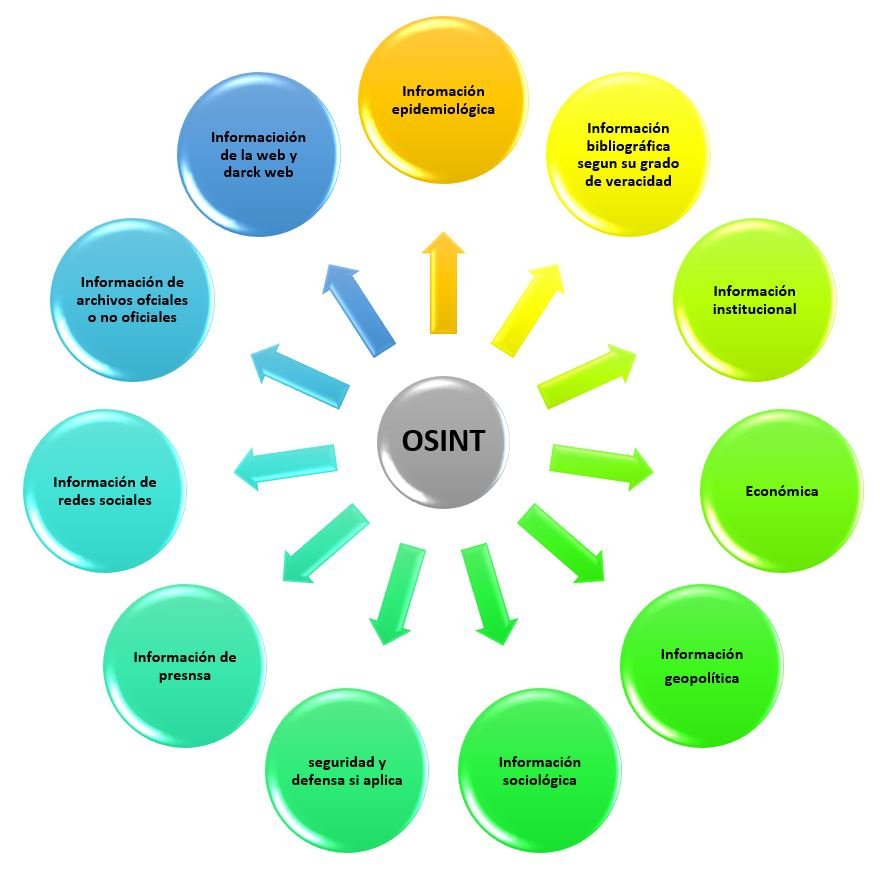
- 2.Information from open sources (OSINT) The National Institute of Public Administration (INAP) defines open source as "like any type of information" whether printed, digital, analog and that can be transmitted or obtained from various sources of open consultation information, such as information media, libraries, social networks, internet, etc. The origin of open sources is listed in Figure 3
- Information on WHO regional offices and by country.
- Active Surveillance: Regular monitoring of information sources requires a highly trained epidemiology specialist with experience in handling information.
- Passive Surveillance: Routinely report the information generated to detect a case early.
- Classic Surveillance: It is carried out routinely, reporting cases of diseases, based mainly on the reports of the health institutions of the three levels of care. The big disadvantage is the slow detection of outbreaks and emerging threats.
- Event-based surveillance: Information obtained from intelligence sources that can help detect events that occur in populations without access to formal health services. As soon as an event occurs, it is reported, and the risk assessment protocol must be initiated(36).
In addition to the management of technological platforms of information systems in real-time and telecommunications, whether at the state, national or international level, to obtain information or data that lead to having elements to obtain the necessary health intelligence(37).
PROCESSING AND ANALYSIS
Once the information and data are available, the measurement of veracity and its analysis continue,
previously the veracity and degree of evidence of the information must be checked, for which different
tools will(37,38).
One One of the problems they will face in order to discriminate a large amount of information is that it
is influenced by Hick's law(39).
Subsequently, the analysis of the information from the database and/or hard information will be
carried out, such as the data of:
- Indicators
- Rates
- Endemic channels
- Specific national and international epidemiological
- Information Hard data from verbal autopsies(39)
In general, they will be the databases that were mentioned previously, and the expertise of the analysts
who will be able to use various methods of information analysis that can be summarized as
follows(40):
Structured analytical techniques for the analysis of information for products of intelligence.
Structured analysis is defined as a “differentiated intelligence analysis methodology that is
carried out step by step to process all kinds of incomplete, ambiguous and sometimes misleading
information that analysts have to deal with”(41).
Structured analysis is defined as a “differentiated intelligence analysis methodology that is
carried out step by step to process all kinds of incomplete, ambiguous and sometimes misleading
information that analysts have to deal with” .
There are the following categories of analysis, expert judgment, structured analysis, and
quantitative methods using empirical data.
Structured analysis methods: Structured
- Brainstorming
- Impact matrix Cross
- Check Key assumptions
- Indicators
- Analysis of competing hypotheses
- Structured analysis and self-criticism
- What if analysis (41)
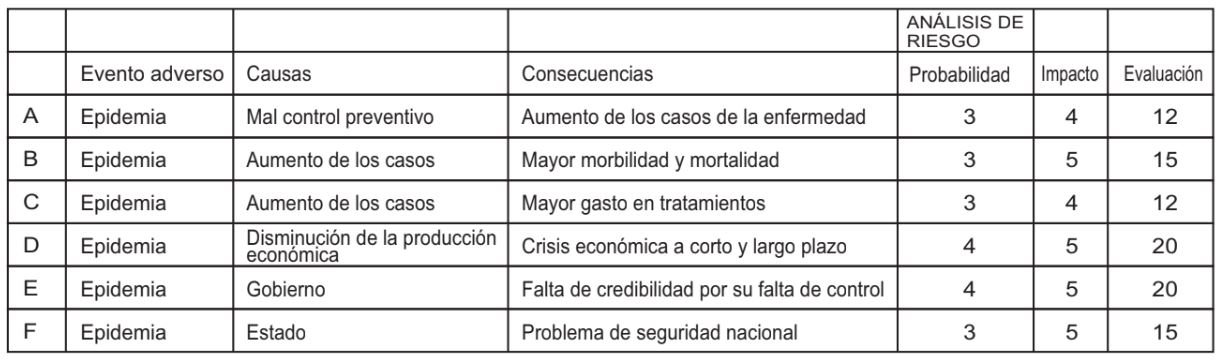
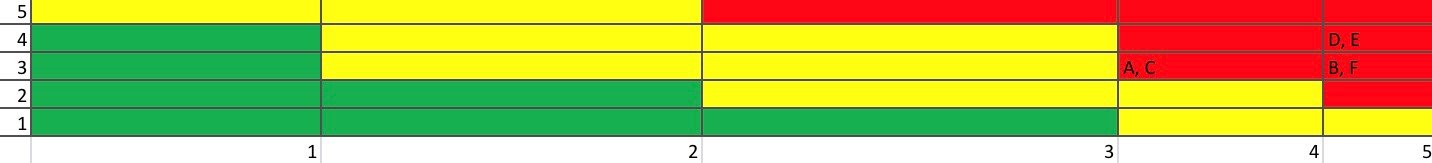
It is probably one of the most used methods in the health area and comprehensive disaster risk management.It is assumed that there is no 100 percent securit therefore there will always be a risk. Risk is the possibility that a future event will cause a negative impact or harm; and the factors that form a risk are the threat that is the latent intention of an individual, group of people or the latent danger of a disturbing phenomenon of harming or causing serious harm to people, facilities, heritage, to the information of an institution, company or individual; it can be specified or dissuaded depending on the degree of preparation (prevention) or response (mitigation) if the response capacity of the organization, society, etc. is exceeded(42).
Based on the information previously processed and available, the frequency with which events can occur and the magnitude of their consequences will be determined. The knowledge that is generated allows proposing lines of action for the prevention, containment, care, and monitoring of risks; both for national security and to determine the latent risks in the health sector, of a hospital, a hospital service, or a patient, as well as for the interests of a company or corporation(43,44).
After having analyzed all these factors, we can measure them through any of these methods(48):
- By the degree of existing vulnerability
- The degree of occurrence
- The degree of impact
Network of links
The Network of links, this applies to all sectors of society, is not exclusive to criminology
and crime investigation; Although it is used more for criminal aspects and crime prevention, having
knowledge about the subject can help us improve our business or, in the case of the health sector, to
find the tools to make security efficient(42).
A network is a set of individuals that, individually or as a group, are related to each other
for a specific purpose, characterized by the existence of information flows. Networks can have few or
many elements that interact with each other and one or more kinds of relationships between them. A
network is composed, therefore, of three basic elements which are: nodes or actors, links or
relationships, and flows.(43).
The use of link networks allows us to know the actors, nodes, or agents that make them up, the
relationships that are woven between them, and the micro and macro-social processes that arise from that
convergence. Through a network of links we can trace, for example, an infected carrier and all the
contacts (links) he has had in a certain period of time, this allows us to safely track all those
possible contacts Center for research and national security (with the possibility of deloping the same
disease.
In fact, in 2009 the defunct Center for Research and National Security (CISEN) traced the
"patient" from Veracruz, finding that the primary contagion really came from abroad . A technique that
today would be very useful in the traceability of COVID 19 to carry out a risk analysis and have a
perspective and impact based on all the links, medical intelligence at its best .(44,45).
REALIZATION OF THE LINES OF ACTION AND PROSPECTIVE SCENARIOS
Formulation of the proposal of lines of action
Once we have the results of the analysis of the information and the risks, we must propose and
initiate the lines of action for the immediate intervention on the phenomenon and the vulnerabilities,
to avoid as much as possible the impact on the health sector and its different ramifications affecting
other sectors, complying with the following steps(49):
- What to do? to solve the problem from the perspective of the State or the health sector or organization
- Formulation of strategies for public policies in health
- Formulation of action strategies in the health sector
- Assignment of persons in charge and deadlines(46)
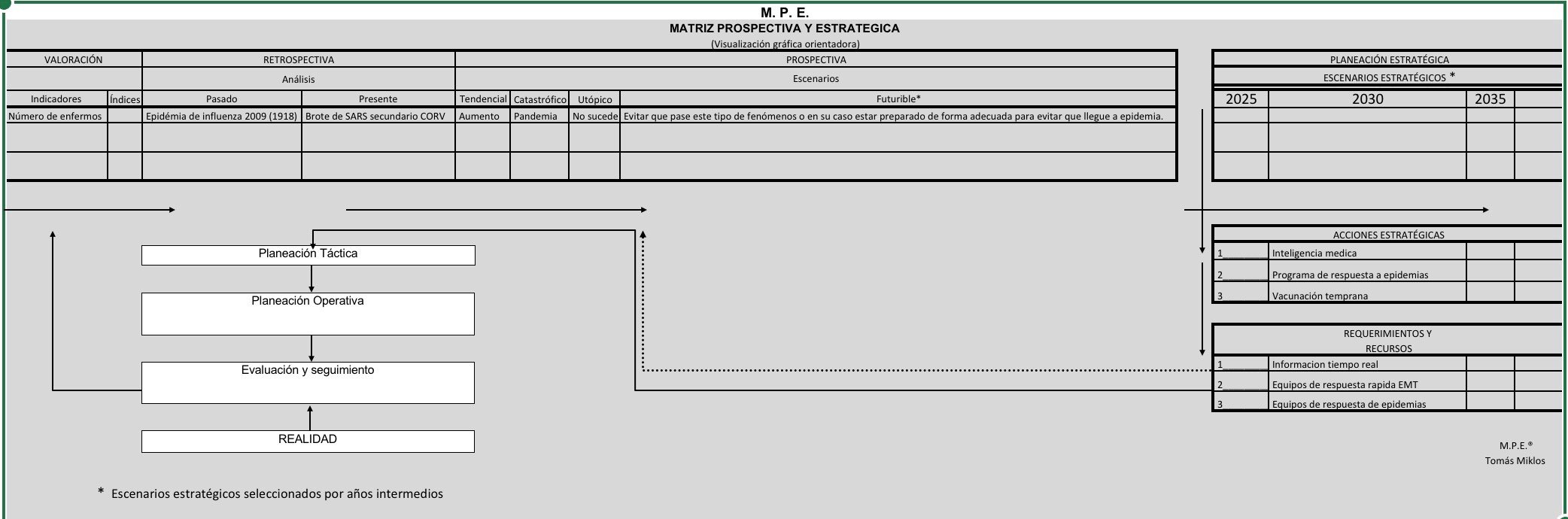
Construction of prospective scenarios
Having the lines of action, the analysis from the information as well as the historical
antecedents it will be possible to formulate forecasts and design scenarios and outcomes according to
the facts and tendencies that may occur; as well as their impacts or possible repercussions in the
short, medium and long term. (47,48)
It is always thought that the construction of scenarios is to have a perspective of the probable
future and practically without any alternative. But it is not like that, the construction of scenarios
allows us to delimit possible alternatives and identify situations that in the future could cause us
problems; and strategies, interventions, and policies to avoid this possibility.
The construction of scenarios helps to determine what can happen, not what is going to happen,
or what must happen, or even what people want to happen.
Scenarios can be divided into different types, but the most common are:
- Trend
- Future
- Catastrophic
- Utopian(49)
RISK AGENDA AND DECISION-MAKING (DISSEMINATION AND EXPLOITATION)
Risk agenda
After formally identifying the risks, the lines of action, and the possible scenarios, the risk
agenda will be drawn up, which is the executive instrument of strategic planning, which is the result;
and the issues identified by the analysts to be addressed and analyzed by the decision-maker are stated,
and that the health sector must attend to follow up on their behavior or evolution(52)
Let us remember that the risk agenda has two main lines of action:
- It is the governing document of the activities of the intelligence area in Health and of a decision-maker.
- It is the basic tool for strategic planning of intelligence in health since it organizes and delimits the universe of work of the areas that comprise it.
Normative
- The agenda allows programming and gives priorities and resources to each one of the attention topics, according to their level of risk of importance and possibility of occurrence.
- The foregoing allows more efficient use of the resources of the health intelligence service, the ministries of health and/or hospitals, focusing them on covering the information needs of the institutional users.
- The risk agenda establishes the scenarios in which health care situations will foreseeably develop in a given period of time
- It is an explanatory and projective intelligence exercise that seeks to establish, through analysis, the future development of problems social and political policies of the health sector that are likely to become risks for the stability and tranquility of the sector and its ramifications towards other sectors such as the economic, political, social, security, etc.
The usefulness and value that decision-makers grant to the agenda are essential to guide the activities of the service that works on it and therefore of the hospital, the organization, or the health intelligence service(54).
Functions of the Health Intelligence risk agenda.
Suggested structure for the Health Risk Agenda
- Background
- Problem
- Risk
- Analysis Critical failure mode and effect (ACMEF) (Identification of risks)
- Hierarchical Analysis of Processes (Risk Hierarchy)
- AGENDA
- Risk
- Responsible
- Interventions
- Results
- Evaluation (indicators and/or external evaluators)
Decision making
The teams, strategies and processes that are organized in response to a crisis have many
different names, for example: “Crisis Response Team”, “COVID-19 Task Force”, “Outbreak Management Team”,
“War Room”, “Emergency Coordination Command Center”, “Disaster Management Committee” ", among others.
However, their organization and objectives are often similar. They are a group of people who make up the
central decision-making body in response to a crisis. These decision-making bodies in crisis situations
have three purposes(53):
- Facilitate rapid decision-making To.
- Speed up the collection, provision, and dissemination of essential information
- To ensure coordination and collaboration between key stakeholders.
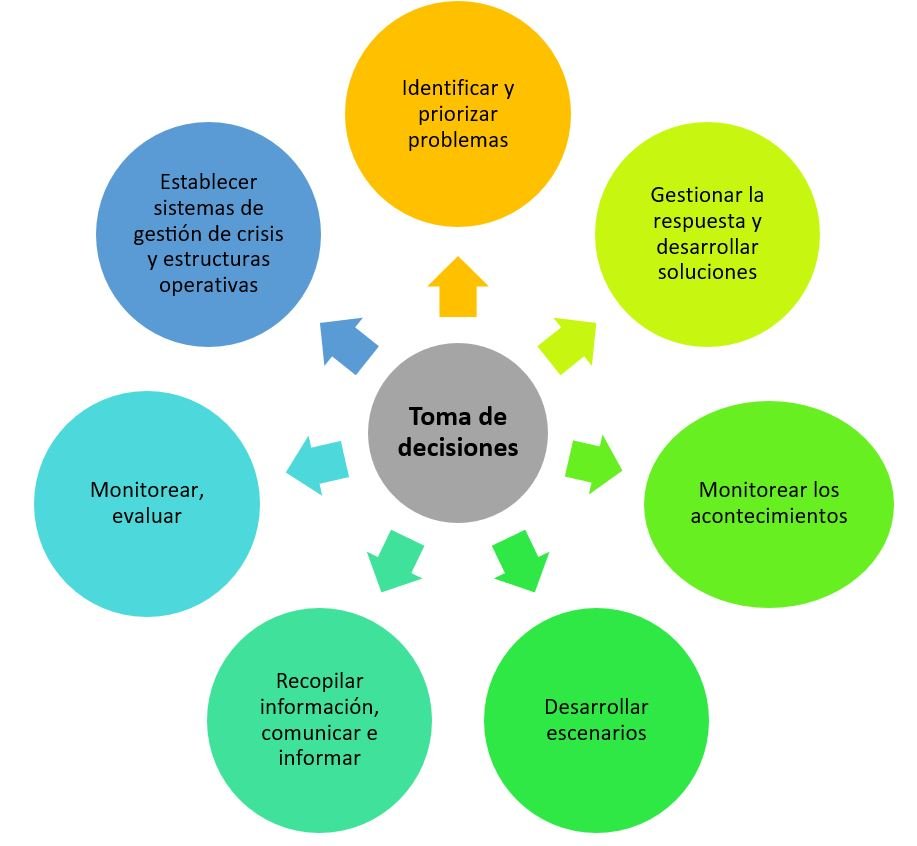
Decision-making based on the risk agenda, scenarios, and lines of action must be carried out according to the following scheme(55):
EXPECTED HEALTH INTELLIGENCE PRODUCTS
The expected products of a health intelligence system will be subject to the risk agenda, the line of action of the sector, and the country's public policies, but we can summarize them as follows(56):
- Medical operational intelligence, which will serve for decision-making with critical analysis and will integrate appropriately, for example, in emergency services in units critical decisions.(57,49)
- Realization of perspective and/or multidimensional scenarios that directly or indirectly affect the health sector.
- Perform multicausal longitudinal and vertical monitoring of morbidity and mortality processes in a critical sense with a multidimensional vision.
- Real-time monitoring of patients preventively (Analysis of vulnerabilities for the spread of infectious diseases) or contagious and/or chronic
- Risk estimates (based on a set of variables/user) in certain conditions.
- Realization of predictive and/or projective models of infectious-contagious or chronic-degenerative diseases with a high social, economic, political, and human security impact(58).
- Census of patients with priority diseases.
- Obtaining information on social networks through the use of free-text search engines(51).
- Development of information products through dashboards (various visualizations), dynamic query tools (reports, dynamic cubes, data mining).
- Advanced analytics projects, such as disease prediction, complication risk prediction, calculation of surgical priority, identification of potential risks in public health, predictive health analytics, treatment analytics, and diagnoses to improve the cure of chronic and degenerative diseases.
- Develop models and simulations of the behavior of potential health risks to carry out projective and predictive scenarios that serve the decision-maker in his decision-making. (59)
- Carry out, based on the results of the analysis, the lines of action for prevention and mitigation that could be taken.(60)
- Carry out demographic profiles that support health decisions.
CONCLUSIONS
The generation of Health Intelligence information implies the linking of information from the field of
health (such as morbidity and mortality) with the integration of sources from different sectors, such as
social, environmental, cultural, political, economic, security, communications, and related to
infrastructure. The generation of health intelligence products requires three important factors: highly
qualified personnel in health referral intelligence methodology, the existence of a timely and reliable
quality information system, and technological support that performs advanced analysis processes.
An Intelligence in Health organization must start from the premise of having complete, precise,
and adequate diagnoses, which include the problems of the living conditions and health of the
population, guided by the multidimensional indicator of poverty, for which it must consider the problem
of that moment that revolves around non-prioritized health care, the inadequate use of health resources,
the existence of vulnerable and unprotected population groups, the poorly designated health offer,
problems of poor health administration and a poor and weak management, a low capacity to manage and
prevent the main risks and damages to health.
With all this data and information to be able to use the aforementioned steps to obtain an
intelligent, assertive, efficient, prospective, and projective product that guides and helps
decision-makers of the high, medium, and low levels to make decisions in the realization of health
policies.
Authorship contributions: All authors participated in the research, through the
development of the project, collection, and analysis of information, as well as in the
preparation of the manuscript of this research.
Funding sources: Self-financed.
Conflicts of Interest: None of the authors has a conflict of interest, in accordance with
their declaration.
Received: December 06, 2021
Approved: February 13, 2022
Correspondence: Augusto Flavio Figueroa Uribe
Address: Hospital Pediátrico Peralvillo SSCDMX, Calz San Simon 14, San Simón
Tolnahuac, Cuauhtémoc, 06920 Tolnahuac, CDMX – México.
Telephone number: 555 427 275 164
E-mail: mandolarian1975@gmail.com
REFERENCIAS