ARTÍCULO DE REVISIÓN
REVISTA DE LA FACULTAD DE MEDICINA HUMANA 2021 - Universidad Ricardo PalmaDOI 10.25176/RFMH.v21i1.3119
FACTORES DE RIESGO ASOCIADOS A ESÓFAGO DE BARRETT EN PACIENTES HOSPITALIZADOS
RISK FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH BARRETT'S ESOPHAGUS IN HOSPITALIZED PATIENTS
Gerard Gomez1
1Instituto de Investigación en Ciencias Biomédicas, Universidad Ricardo Palma, Lima, Perú.
Objetivo: El objetivo de este artículo es realizar una revisión sistemática de artículos científicos que revelen los factores de riesgo asociados a Esófago de Barret en pacientes hospitalizados. Métodos: La revisión fue efectuada mediante búsqueda electrónica de artículos relacionados a factores de riesgo asociadas a Esófago de Barret en pacientes hospitalizados. La pregunta PEO fue ¿Cuáles son los factores de riesgo asociados a Esófago de Barret en pacientes hospitalizados? Las fuentes de búsqueda fueron en PUBMED. Los términos de búsqueda fueron: Factores de Riesgo; Esófago de Barret; pacientes hospitalizados. Para esta revisión se seleccionaron los artículos publicados a partir el año 2010 que tuvieron experiencias investigativas y aspectos teórico-conceptuales. Resultados: De los 389 resultados encontrados con fuentes de indexación, se seleccionaron un total de 25 artículos donde 22 artículos contenían resultados de investigación y 3 fueron considerados para aspectos teórico – conceptuales que se relacionan con el propósito del estudio. La búsqueda dio como resultado factores de riesgo asociados a Esófago de Barret según las características demográficas y rasgos del paciente, presentación y datos clínicos y estilos de vida. Conclusión: Se evidencia una asociación de diversos factores de riesgo con Esófago de Barret en pacientes hospitalizados. Los factores de riesgo asociados a Esófago de Barret en la revisión que fueron más concordantes son sexo masculino, edad incrementada, síndrome metabólico, hernia hiatal, uso de inhibidores de bomba de protones, reflujo gastroesofágico(RGE), apnea obstructiva del sueño y esofagitis erosiva.
Palabras Clave: Factores de Riesgo, Esófago de Barret, Pacientes.(Fuente: DeCS BIREME)
ABSTRACT
Objective: The objective of this article is to carry out a systematic review of scientific articles that reveal the risk factors associated with Barret's esophagus in hospitalized patients. Methods: The review was performed by electronic search for articles related to risk factors associated with Barret's esophagus in hospitalized patients. The PEO question was: What are the risk factors associated with Barret's esophagus in hospitalized patients? The search sources were in PUBMED. The search terms were: Risk Factors; Barret's esophagus; hospitalized patients. For this review, articles published from 2010 that had research experiences and theoretical-conceptual aspects were selected. Results: Of the 389 results found with indexing sources, a total of 25 articles were selected where 22 articles contained research results and 3 were considered for theoretical-conceptual aspects that are related to the purpose of the study. The search resulted in risk factors associated with Barret's esophagus according to demographic characteristics and patient traits, presentation, and clinical data and lifestyles. Conclusion: An association of various risk factors with Barret's esophagus is evidenced in hospitalized patients. The most concordant risk factors associated with Barret's esophagus in the review were male sex, increased age, metabolic syndrome, hiatal hernia, use of proton pump inhibitors, gastroesophageal reflux (GER), obstructive sleep apnea, and erosive esophagitis.
Key words: Risk Factors, Barret's Esophagus, Patients. (Source: MeSH NLM)
En la actualidad hay diversos factores riesgos de Esófago de Barret que no han sido revisados en su totalidad en pacientes hospitalizados. El esófago de Barrett es una afección esofágica adquirida que se caracteriza por la presencia de epitelio columnar metaplásico en el esófago distal que reemplaza a la mucosa escamosa estratificada normal. Los factores asociados con el esófago de Barrett son los síntomas de la enfermedad por reflujo gastroesofágico (ERGE), la edad avanzada y el género masculino. Estudios han revelado una asociación con la obesidad central (relación cintura / cadera o circunferencia abdominal, pero menos claramente con el índice de masa corporal o el contenido general de grasa corporal), el tabaquismo, la raza caucásica y una historia familiar positiva. Por el contrario, el consumo de alcohol no parece ser un factor de riesgo importante. Estudios también han encontrado posibles factores de riesgo, como el síndrome metabólico, la diabetes mellitus tipo 2 y la apnea del sueño.(1)
Un mecanismo potencial de la patogénesis de BE implica la transdiferenciación, en la cual las células escamosas esofágicas completamente diferenciadas cambian a células columnares completamente diferenciadas, ya sea directamente (sin sufrir una división celular) o indirectamente (a través de la división celular). Aunque las células diferenciadas una vez se consideraron inmutables, los estudios han demostrado que las células diferenciadas pueden reprogramarse para adquirir características de células progenitoras inmaduras. Muchos tipos de células maduras tienen la capacidad de desdiferenciarse en células con características de células progenitoras. Por lo tanto, la transdiferenciación en el esófago puede ocurrir a través de un proceso de ERGE de 2 etapas en una reprogramación inducida en la que las células escamosas maduras invierten su diferenciación para adquirir plasticidad de células progenitoras antes de cambiar a un fenotipo columnar.(2)
El diagnóstico del esófago de Barrett aparentemente debería ser sencillo, es decir, un cambio visible en el revestimiento de la esófago distal y confirmación histológica con metaplasia columnar. Los componentes del diagnóstico del esófago de Barrett abarcan el reconocimiento endoscópico, las biopsias apropiadamente dirigidas y la confirmación histológica.(3)
El objetivo de este artículo es realizar una revisión sistemática de artículos científicos que revelen los factores de riesgo asociados a Esófago de Barret en pacientes hospitalizados.
MÉTODOS
La revisión fue efectuada mediante búsqueda electrónica de artículos relacionados con factores de riesgo de Esófago de Barret, en la fuente de indexación de PUBMED. La pregunta PEO fue ¿Cuáles son los factores de riesgo asociados a Esófago de Barret en pacientes hospitalizados?
Los términos de búsqueda avanzada para PUBMED fueron: factores de Riesgo, Esófago de Barret y pacientes. Para esta revisión se seleccionaron los artículos publicados con resultados de investigación y aquellos con aspectos teórico-conceptuales desde junio 2010 y realizado en humanos con ayuda de la búsqueda avanzada de PUBMED. La búsqueda sistemática utilizada en PUBMED fue: ((Patients[tiab] OR patient[tiab] OR Clients[tiab] OR Client[tiab]) AND (risk factors[tiab] OR Factor, Risk[tiab] OR Factors, Risk[tiab] OR Risk Factor[tiab] OR Population at Risk[tiab] OR Risk, Population at[tiab] OR Populations at Risk[tiab] OR Risk, Populations at[tiab] AND (Barrett Metaplasia[tiab] OR Barrett Metaplasias[tiab] OR Metaplasia, Barrett[tiab] OR Metaplasias, Barrett[tiab] OR Barrett's Syndrome[tiab] OR barrett Syndrome[tiab] OR Barrett Syndrome[tiab] OR Barrett's Esophagus[tiab] OR barrett Esophagus[tiab] OR Esophagus, Barrett's[tiab] OR Esophagus, Barrett[tiab] OR Barrett Epithelium[tiab] OR Epithelium, Barrett)). La Figura 1 muestra el proceso de selección de los términos para la búsqueda sistemática.
Tabla 1. Proceso de selección de los términos para la búsqueda sistemática PUBMED.
| DeCS | MeSH | MeSH + Entry terms | ||
| P | Participantes | Pacientes | “patient” [Mesh] | Patients[tiab] OR patient[tiab] OR Clients[tiab] OR Client[tiab] |
| E | Exposición | Factor de riesgo | “risk factors” [Mesh] | Risk factors[tiab] OR Factor, Risk[tiab] OR Factors, Risk[tiab] OR Risk Factor[tiab] OR Population at Risk[tiab] Pr Risk, Population at[tiab] Or Populations at Risk[tiab] OR Risk, Populations at[tiab] |
| O | Outcome | Esófago de Barret | “Barrett Esophagus” [Mesh] |
(Barret Metaplasia[tiab] OR Barrett Metaplasias[tiab] OR Metaplasia, Barrett[tiab] OR Metaplasias, Barrett[tiab] OR Barrett’s Syndrome[tiab] OR barrett Syndrome[tiab] OR Barrett Syndrome[tiab] OR Barrett’s Esophagus[tiab] OR barrett Esophagus[tiab] OR Esophagus, Barrett’s[tiab] OR Esophagus, Barrett[tiab] OR Esophagus, Barrett[tiab] OR Barrett Epithelium[tiab] OR Epithelium, Barrett)) |
Los criterios de exclusión fueron los artículos no acordes al tema de revisión y sin valores de medida de asociación (RR, OR, HR).
RESULTADOS
Se obtuvieron un total 389 resultados en la búsqueda sistemática encontrados en PUBMED y se seleccionaron un total de 25 artículos donde 22 artículos contenían resultados de investigación y 3 fueron considerados para aspectos teórico – conceptuales que se relacionan con el propósito del estudio. La Figura 2 muestra el proceso de selección de artículos en PUBMED.
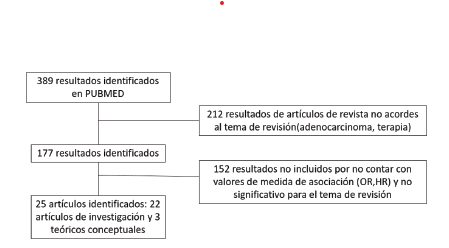
Figura 1. Proceso de selección de artículos de investigación y teórico-conceptuales para el articulo de revisión en PUBMED
La búsqueda dio como resultado factores de riesgo asociados a Esófago de Barret según las características demográficas y rasgos del paciente, presentación y datos clínicos y estilos de vida.
La Tabla 2, muestra los factores de riesgo para Esófago de Barret en pacientes hospitalizados de estudios observacionales de cohorte y casos y controles seleccionados para el artículo de revisión.
Tabla 2. Factores de riesgo para Esófago de Barret en pacientes hospitalizados de estudios observacionales de cohorte y casos y controles.
| FACTOR DE RIESGO MEDIDO | AUTOR | TIPO DE ESTUDIO | ARTICULO | POBLACION | VALOR DE MEDIDA | IC 95% | P |
| Caracteristicas demograficas y rasgos del paciente (Edad, Sexo,etnia,IMC) | |||||||
| Sexo masculino | Yousaf Bashir Hadi(4) | Casos y controles | Independent association of obstructive sleep apnea with Barrett’s esophagus |
1091 | OR:1.71 | 1.13–2.59 | <0.01 |
| Sexo masculino | Emery C Lin(5) | Estudio de cohorte | Low Prevalence of Suspected Barrett’s Esophagus in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Without Alarm Symptoms |
4122 | OR:2.61 | 2.44 - 2.79 | |
| Sexo masculino | Yan-Hua Chen(6) | Estudio de cohorte | Prevalence and risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus in Taiwan | 3385 | OR:2.106 | 1.145-3.872 | 0.017 |
| Sexo masculino | A. Sonnenberg(7) | Casos y control | The influence of Helicobacter pylori on the ethnic distribution of Barrett’s metaplasia |
596 479 | OR: 3.34 | 3.28–3.40 | <0.0001 |
| Sexo masculino | Theresa H. Nguyen(8) | Casos y control | Risk Factors for Barrett’s Esophagus Compared Between African Americans and Non-Hispanic Whites | 1952 | OR:3.35 | 1.51–7.43 | 0.003 |
| Sexo masculino | K. Keyashian(9) | Casos y control | Barrett’s esophagus in Latinos undergoing endoscopy for gastresophageal reflux disease symptoms |
663 | OR:2.34 | 1.35–4.05 | 0.002 |
| Sexo femenino | Matheus Degiovani(10) | Casos y control | Is there a relation between helybacter pylori and intestinal metaplasia in short column epitelization up to 10 mm in the distal esophagus? |
373 | OR:1.76 | 1.13 - 2.76 | 0.013 |
| Edad incrementada | Yousaf Bashir Hadi(4) | Casos y controles | Independent association of obstructive sleep apnea with Barrett’s esophagus |
1091 | OR:1.04 | 1.02–1.06 | <0.01 |
| Edad incrementada | Atsuhiro Masuda(11) | Estudio de cohorte | Influence of hiatal hernia and male sex on the relationship between alcohol intake and occurrence of Barrett’s esophagus | 8031 | OR:1.42 | 1.23–1.64 | <0.0001 |
| Edad incrementada | Matheus Degiovani(10) | Casos y control | IS THERE A RELATION BETWEEN HELYBACTER PYLORI AND INTESTINAL METAPLASIA IN SHORT COLUMN EPITELIZATION UP TO 10 MM IN THE DISTAL ESOPHAGUS? |
373 | OR:1.017 | 1.001 -1.033 | 0.031 |
| Edad incrementada | Yan-Hua Chen(6) | Estudio de cohorte? | Prevalence and risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus in Taiwan | 3385 | OR:1.033 | 1.012-1.055 | 0.002 |
| Edad incrementada | Rena Yadlapati(12) | Estudio de cohorte | Reduced Esophageal Contractility Is Associated with Dysplasia Progression in Barrett’s Esophagus: A Multicenter Cohort Study | 193 | OR:1.08 | 1.01-1.16 | 0.03 |
| Edad incrementada | Wytske M. Westra(13) | Casos y controles (Usuarios de cigarrillo y tabaco no fumable vs No usuarios) | Smokeless Tobacco and Cigar and/or Pipe Are Risk Factors for Barrett Esophagus in Male Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease | 1015 | OR:1.06 | 1.05-1.08 | <.001 |
| Edad incrementada | Wytske M. Westra(13) | Casos y controles (Usuarios de cigarrillo y cigarro vs No usuarios) | Smokeless Tobacco and Cigar and/or Pipe Are Risk Factors for Barrett Esophagus in Male Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease | 1015 | OR:1.06 | 1.05-1.08 | <.001 |
| Edad incrementada | A. Sonnenberg(7) | Casos y control | The influence of Helicobacter pylori on the ethnic distribution of Barrett’s metaplasia |
596 479 | OR: 18.29 | 17.39–19.24 | <0.0001 |
| Edad incrementada | K. Keyashian(9) | Casos y control | Barrett’s esophagus in Latinos undergoing endoscopy for gastresophageal reflux disease symptoms |
663 | OR:2.17 | 1.25–3.76 | 0.006 |
| Edad incrementada | Gloria Vargas Cárdenas(14) | Casos y control | Esófago de Barrett: Prevalencia y Factores de Riesgo en el Hospital Nacional “Arzobispo Loayza” Lima-Perú |
11,970 | OR: 2.57 | 1.41-4.69 | 0.001 |
| Edad de 40 a 49 años | Emery C Lin(5) | Estudio de cohorte | Low Prevalence of Suspected Barrett’s Esophagus in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Without Alarm Symptoms |
4122 | OR:1.32 | 1.18 - 1.47 | |
| Edad de 50 a 59 años | Emery C Lin(5) | Estudio de cohorte | Low Prevalence of Suspected Barrett’s Esophagus in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Without Alarm Symptoms |
4122 | OR:1.54 | 1.39 - 1.71 | |
| Edad de 60 a 69 años | Emery C Lin(5) | Estudio de cohorte | Low Prevalence of Suspected Barrett’s Esophagus in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Without Alarm Symptoms | 4122 | OR:1.68 | 1.51 - 1.87 | |
| Edad >=70 años | Emery C Lin(5) | Estudio de cohorte | Low Prevalence of Suspected Barrett’s Esophagus in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Without Alarm Symptoms | 4122 | OR:1.42 | 1.25 - 1.61 | |
| IMC mayor de 25 | Hirohiko Shinkai(15) | Casos y control | Association between the Body Mass Index and the Risk of Barrett’s Esophagus in Japan |
113 | OR: 3.45 | 1.30–9.13 | <0.01 |
| Noreuropeo | A. Sonnenberg(7) | Casos y control | The influence of Helicobacter pylori on the ethnic distribution of Barrett’s metaplasia | 596 479 | OR: 1.14 | 1.03–1.26 | 0.0117 |
| Presentación y datos clínicos (antecedentes medicos) | |||||||
| Sindrome metabolico | Shou-Wu Lee(16) | Casos y control | Association of metabolic syndrome with erosive esophagitis and Barrett’s esophagus in a Chinese population | 7712 | OR:2.82 | 2.05-3.88 | <0.001 |
| Sindrome metabolico | Cadman L. Leggett(17) | Casos y controles EB VS con ERGE |
Metabolic Syndrome as a Risk Factor for Barrett Esophagus: A Population-Based Case-Control Study |
309 | OR:2 | 1.1-3.6 | 0.02 |
| Sindrome metabolico | Cadman L. Leggett(17) | Casos y controles EB vs sin ERGE |
Metabolic Syndrome as a Risk Factor for Barrett Esophagus: A Population-Based Case-Control Study |
309 | OR:1.9 | 1.03-3.6 | 0.04 |
| Obesidad central | Chih-Cheng Chen(18) | Casos y control | Central Obesity and H. pylori Infection Influence Risk of Barrett’s Esophagus in an Asian Population | 161 | OR:2.79 | 1.89–4.12 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | K. Keyashian(9) | Casos y control | Barrett’s esophagus in Latinos undergoing endoscopy for gastresophageal reflux disease symptoms | 663 | OR:2.23 | 1.10–4.53 | 0.03 |
| Hernia hiatal | Camille Bazin(19) | Casos y control | Esophageal Motor Disorders Are a Strong and Independant Associated Factor of Barrett’s Esophagus | 201 | OR:5.60 | 2.45-12.76 | < 0.001 |
| Hernia hiatal | Atsuhiro Masuda(11) | Estudio de cohorte | Influence of hiatal hernia and male sex on the relationship between alcohol intake and occurrence of Barrett’s esophagus | 8031 | OR:3.37 | 2.50–4.59 | <0.0001 |
| Hernia hiatal | Emery C Lin(5) | Estudio de cohorte | Low Prevalence of Suspected Barrett’s Esophagus in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Without Alarm Symptoms |
4122 | OR:1.60 | 1.50 - 1.70 | |
| Hernia hiatal | Yan-Hua Chen(6) | Estudio de cohorte? | Prevalence and risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus in Taiwan | 3385 | OR:3.037 | 1.765-5.225 | < 0.001 |
| Hernia hiatal | Praveen Mathew(20) | Casos y control | Risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus in Indian patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease |
278 | OR:3.14 | 1.2–8.17 | 0.01 |
| Hernia hiatal menos de 3cm | Theresa H. Nguyen(8) | Casos y control | Risk Factors for Barrett’s Esophagus Compared Between African Americans and Non-Hispanic Whites |
1952 | OR:2.79 | 1.85–4.19 | <0.001 |
| Hernia hiatal mayor o igual a 3cm | Theresa H. Nguyen(8) | Casos y control | Risk Factors for Barrett’s Esophagus Compared Between African Americans and Non-Hispanic Whites |
1952 | OR:5.08 | 3.35–7.69 | <0.001 |
| Hernia hiatal | Hirohiko Shinkai(15) | Casos y control | Association between the Body Mass Index and the Risk of Barrett’s Esophagus in Japan |
113 | OR:18.3 | 7.21–46.5 | <0.01 |
| Gatritis activa(antro) | Theresa H. Nguyen(8) | Casos y control | Risk Factors for Barrett’s Esophagus Compared Between African Americans and Non-Hispanic Whites |
1952 | OR:1.73 | 1.10–2.73 | 0.02 |
| Uso de bomba de inhibidor de protones | Theresa H. Nguyen(8) | Casos y control | Risk Factors for Barrett’s Esophagus Compared Between African Americans and Non-Hispanic Whites |
1952 | OR:1.88 | 1.40–2.52 | <0.001 |
| Uso de bomba de inhibidor de protones | Hirohiko Shinkai(15) | Casos y control | Association between the Body Mass Index and the Risk of Barrett’s Esophagus in Japan |
113 | OR:8.28 | 2.96–123.1 | 0.01 |
| Presencia de eructos | Praveen Mathew(20) | Casos y control | Risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus in Indian patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease |
278 | OR:2.28 | 1.11–4.66 | 0.02 |
| Desorden motor de esófago | Camille Bazin(19) | Casos y control | Esophageal Motor Disorders Are a Strong and Independant Associated Factor of Barrett’s Esophagus | 201 | OR:4.49 | 1.85-10.93 | <0.001 |
| RGE | Yousaf Bashir Hadi(4) | Casos y control | Independent association of obstructive sleep apnea with Barrett’s esophagus |
1091 | OR:2.23 | 1.45–3.49 | 0.01 |
| RGE | Cadman L. Leggett(21) | Casos y control | Obstructive Sleep Apnea Is a Risk Factor for Barrett’s Esophagus | 7482 | OR:3.4 | 1.9–6.0 | <.0001 |
| RGE | Jiro Watari(22) | Casos y control (Casos vs no PPI) | Association between obesity and Barrett’s esophagus in a Japanese population: a hospital-based, cross-sectional study |
1581 | OR:3.48 | 1.89–6.41 | <0.0001 |
| RGE | Jiro Watari(22) | Casos y control (Casos vs PPI) | Association between obesity and Barrett’s esophagus in a Japanese population: a hospital-based, cross-sectional study |
1581 | OR:5.67 | 2.17–14.86 | 0.0004 |
| Edad de presentación de síntoma de RGE menor de 30 años | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Población) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
317 | OR:2.93 | 1.67-5.15 | |
| Edad de presentación de síntoma de RGE menor de 30 años | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Pacientes con RGE) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
316 | OR:1.93 | 1.15-3.22 | |
| Síntomas nocturnos de RGE | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Población) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
317 | OR:5.40 | 3.81-7.72 | |
| Sensación de atoramiento | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Población) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
317 | OR:3.00 | 2.13-4.24 | |
| Historia familiar de RGE | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Población) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
317 | OR:2.55 | 1.80-3.62 | |
| Historia familiar de BE | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Población) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
317 | OR:10.08 | 2.83-35.84 | |
| Historia familiar de BE | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Pacientes con RGE) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
316 | OR:3.64 | 1.50-8.83 | |
| 1-2 consultas al año por RGE | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Población) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
317 | OR:7.13 | 4.71-10.81 | |
| Más de 3 consultas al año por RGE | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Población) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
317 | OR:5.12 | 2.96-8.83 | |
| 3-5 consultas al año por cualquier razón | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Población) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
317 | OR:2.06 | 1.40-3.03 | |
| 6-10 consultas al año por cualquier razón | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Población) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
317 | OR:2.69 | 1.65-4.37 | |
| Más de 10 consultas al año por cualquier razón | Omar Bakr(23) | Casos y controles (Casos vs Población) | Gastroesophageal Reflux Frequency, Severity, Age of Onset, Family History and Acid Suppressive Therapy Predict Barrett’s Esophagus in a Large Population |
317 | OR:2.25 | 1.33-3.83 | |
| ADN de virus de papiloma humano | M. YW Wong(24) | Casos y control | Human papillomavirus exposure and sexual behavior are significant risk factors for Barrett’s dysplasia/esophageal adenocarcinoma | 133 | OR:8.2 | 2.8–23.8 | 0.0001 |
| Apnea obstructiva del sueño | Yousaf Bashir Hadi(4) | Casos y control | Independent association of obstructive sleep apnea with Barrett’s esophagus |
1091 | OR:3.26 | 1.72–6.85 | <0.01 |
| Apnea obstructiva del sueño | Cadman L. Leggett(21) | Casos y control | Obstructive Sleep Apnea Is a Risk Factor for Barrett’s Esophagus | 7482 | OR:1.8 | 1.1–3.2 | 0.03 |
| Esofagitis erosiva | Atsuhiro Masuda(11) | Estudio de cohorte | Influence of hiatal hernia and male sex on the relationship between alcohol intake and occurrence of Barrett’s esophagus | 8031 | OR:2.82 | 2.04–3.85 | <0.0001 |
| Esofagitis erosiva | Hirohiko Shinkai(15) | Casos y control | Association between the Body Mass Index and the Risk of Barrett’s Esophagus in Japan |
113 | 15.3 | 3.49–66.8 | 0.01 |
| Esofagitis | Gloria Vargas Cárdenas(14) | Casos y control | Esófago de Barrett: Prevalencia y Factores de Riesgo en el Hospital Nacional “Arzobispo Loayza” Lima-Perú |
11,970 | 14.81 | 3.96- 55.41 | 0.001 |
| Grado B de esofagitis (LA) | Emery C Lin(5) | Estudio de cohorte | Low Prevalence of Suspected Barrett’s Esophagus in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Without Alarm Symptoms |
4122 | OR:2.19 | 1.72 - 2.78 | |
| Grado C/D de esofagitis (LA) | Emery C Lin(5) | Estudio de cohorte | Low Prevalence of Suspected Barrett’s Esophagus in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Without Alarm Symptoms |
4122 | OR:3.50 | 2.59 - 4.73 | |
| Nacimiento prematuro | Seiji Shiota(25) | Estudio de cohorte | Premature Birth and Large for Gestational Age Are Associated with Risk of Barrett’s Esophagus in Adults |
1679 | OR:4.08 | 1.38 – 12.05 | |
| Estilos de vida (relaciones sexuales, consumo de alimentos y bebidas, Tabaco, alcohol) | |||||||
| Persona en una relación sexual | M. YW Wong(24) | Casos y control | Human papillomavirus exposure and sexual behavior are significant risk factors for Barrett’s dysplasia/esophageal adenocarcinoma |
133 | OR:11.4 | 1.4–93.9 | 0.02 |
| Más de 6 parejas sexuales orales | M. YW Wong(24) | Casos y control | Human papillomavirus exposure and sexual behavior are significant risk factors for Barrett’s dysplasia/esophageal adenocarcinoma | 133 | OR:4.0 | 1.2–13.7 | 0.046 |
| Consumo de alcohol | Atsuhiro Masuda(11) | Estudio de cohorte | Influence of hiatal hernia and male sex on the relationship between alcohol intake and occurrence of Barrett’s esophagus | 8031 | OR:1.92 | 1.41–2.61 | <0.0001 |
| Consumo de te caliente | Yan-Hua Chen(6) | Estudio de cohorte | Prevalence and risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus in Taiwan | 3385 | OR:1.695 | 1.043-2.754 | 0.033 |
| Consume siempre cigarrillo | Wytske M. Westra(13) | Casos y controles (Usuarios de cigarrillo y tabaco no fumable vs No usuarios) | Smokeless Tobacco and Cigar and/or Pipe Are Risk Factors for Barrett Esophagus in Male Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease | 1015 | OR:1.43 | 1.06-1.88 | 0.02 |
| Consume siempre cigarrillo y tabaco no fumable | Wytske M. Westra(13) | Casos y controles (Usuarios de cigarrillo y tabaco no fumable vs No usuarios) | Smokeless Tobacco and Cigar and/or Pipe Are Risk Factors for Barrett Esophagus in Male Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease | 1015 | OR:2.53 | 1.22-5.22 | 0.01 |
| Consume siempre cigarrillo | Wytske M. Westra(13) | Casos y controles (Usuarios de cigarrillo y cigarro vs No usuarios) | Smokeless Tobacco and Cigar and/or Pipe Are Risk Factors for Barrett Esophagus in Male Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease | 1015 | OR:1.43 | 1.07-1.91 | 0.02 |
| Consume siempre cigarrillo y cigarro | Wytske M. Westra(13) | Casos y controles (Usuarios de cigarrillo y cigarro vs No usuarios) | Smokeless Tobacco and Cigar and/or Pipe Are Risk Factors for Barrett Esophagus in Male Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease | 1015 | OR:1.90 | 1.03-3.58 | 0.04 |
| Consumo de alimentos grasos | Gloria Vargas Cárdenas(14) | Casos y control | Esófago de Barrett: Prevalencia y Factores de Riesgo en el Hospital Nacional “Arzobispo Loayza” Lima-Perú |
11,970 | OR:8.67 | 2.28-32.99 | 0.001 |
Los factores de riesgo más concordantes por los artículos revisados son sexo masculino, edad incrementada, síndrome metabólico, hernia hiatal, uso de inhibidores de bomba de protones, reflujo gastroesofágico(RGE), apnea obstructiva del sueño y esofagitis erosiva. Obesidad central, diabetes, gastritis activa, presencia de eructos, desorden motor de esófago, ADN de virus de papiloma humano, consumo de alcohol, consumo de tabaco, consumó de té caliente y consumo de alimentos grasos son factores de riesgo con solo un estudio que confirma la asociación con Esófago de Barret los cuales deberían ser más estudiados.
DISCUSIÓN
Según las características demográficas, para diversos autores el sexo masculino es un factor de riesgo de Esófago de Barret(4,5,6,7,8,9). Aunque Matheus Degiovani et al, dice que el sexo femenino es un factor de riesgo de Esófago de Barret(10). Según diversos autores la edad incrementada es un factor de riesgo(4,6,7,9,10,11),12),13),14). Aunque Emery C Lin et al, encontró que el OR incrementa desde los 40 años constantemente hasta los 69 años donde su OR es 1.68.(5)
Con respecto a la presentación y datos clínicos, según Shou-wu Lee et al y Cadman L. Leggett et al, el síndrome metabólico es un factor de riesgo de esófago de Barret.(16,17) Otros autores han encontrado otros componentes de la triada del síndrome metabólico como factores de riesgo como es el caso de Chih -Cheng Chen et al, que nos menciona que la obesidad central es un factor de riesgo de esófago de Barret.(18)
Según varios autores la hernia hiatal es un factor de riesgo de esófago de Barret(5,6,11,19,20). Aunque Theresa H. Nguyen distingue el tamaño de la hernia hiatal considerando que uno mayor o igual a 3 cm es más propenso a tener esófago de Barret.(8)
Según Yousaf Bashir Hadi et al, Cadman L. Leggett et al y Jiro Watari et al, el RGE es un factor de riesgo de esófago de Barret(4,21,22). Aunque Omar Bakr et al, nos menciona que tanto la edad de presentación, los síntomas, la historia familiar y el número de consultas hechas por RGE podrían ser también factores de riesgo.(23) Además, Theresa H. Nguyen et al y Hirohiko Shinkai et al, nos refiere que el uso de inhibidores de bomba de protones es un factor de riesgo de esófago de Barret(8,15).
Según Yousaf Bashir Hadi et al, Cadman L. Leggett et al, la apnea de obstructiva del sueño es un factor de riesgo de esófago de Barret.(4,21)
Según Atsuhiro Masuda et al y Hirohiko Shinkai et al, la esofagitis erosiva es un factor de riesgo de esófago de Barret.(11,15) Aunque para Gloria Vargas Cárdenas et al, solo el hecho de tener esofagitis ya sería un factor de riesgo(14), en cambio para Emery C Lin et al, nos mencionan que solo las esofagitis de grados B, C, D son un factor de riesgo para esófago de Barret5. Los estilos de vida no están tan estudiados como un factor de riesgo por lo cual deberían realizarse mas estudios.
CONCLUSIONES
Se evidencia una asociación de diversos factores de riesgo con Esófago de Barret en pacientes hospitalizados. Los factores de riesgo asociados a Esófago de Barret en la revisión que fueron más concordantes son sexo masculino, edad incrementada, síndrome metabólico, hernia hiatal, uso de inhibidores de bomba de protones, reflujo gastroesofágico(RGE), apnea obstructiva del sueño y esofagitis erosiva.
Contribuciones de Autoría: Los autores participaron en la génesis de la idea, diseño del proyecto, desarrollo, recolección e interpretación de data, análisis de resultados y preparación de manuscrito.
Financiamiento: Autofinanciado.
Conflictos de intereses: Los autores declaran no tener conflictos de interés.
Recibido: 01 de Octubre de 2020
Aprobado: 04 de Diciembre de 2020
Correspondencia: Gerard Gomez.
Dirección: Av. Benavides 5440, Santiago de Surco, Lima-Perú.
Teléfono: +51 952 831 740
Correo: gerardgomez321@gmail.com
REFERENCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS
