ORIGINAL PAPER
JOURNAL OF THE FACULTY OF HUMAN MEDICINE 2020 - Universidad Ricardo PalmaDOI 10.25176/RFMH.v20i3.3170
PROGNOSTIC FACTORS AND SURVIVAL STUDY IN HIGH-GRADE GLIOMA IN A HOSPITAL IN LIMA, PERU
FACTORES PRONÓSTICOS Y ESTUDIO DE SUPERVIVENCIA EN GLIOMA DE ALTO GRADO EN UN HOSPITAL DE LIMA, PERÚ
Paul Méndez-Aguilar1,a, Victor Juan Vera-Ponce2,b
1 Universidad Nacional de Trujillo, Trujillo-Perú
2 Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad Científica del Sur, Lima-Perú.
aNeurosurgeon.
bGeneral practitioner.
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Gliomas are primary tumors of the central nervous system. They are classified from grade I-IV, with high grade III and IV being the most frequent and with poor prognosis. Objective: To determine the prognostic
factors of survival in patients with high-grade gliomas in a hospital in Lima, Peru. Methods: The medical records with high-grade glioma from 2010-2014 were retrospectively reviewed, ten variables were analyzed with Kaplan-Meier and
Log Rank survival graphs and the Cox regression model. Results: Out of a total of 278 patients with high-grade gliomas, 136 were men and 142 women. The analysis of Progression-Free Survival (SLP) had a range of 5.6-80.3 (median 22.7)
and the analysis of overall survival (PS) had a range of 4-83.2 (median 26, 2 months. The overall survival for the IV grade tumor was 15.7 months (95% CI 14.2-17.1); the III degree was 38.4 months (95% CI 35.8-40.9). The grade (PS: HR 15;
SLP: HR 25.1); surgical treatment (PS: HR 0.6; SLP: HR 0.49), age (PS: HR 1.47; SLP: HR 1.7), adjuvant treatment (PS: HR 0.6; SLP: HR 0 , 58) and karnofsky (PS: HR 0.7) were correlated; while the Karnofsky for SLP does not (P = 0.146). Conclusion: age, functional status, surgical treatment, adjuvant treatment, and tumor grade are prognostic factors for PS. In contrast, for SLP the prognostic factors were age, surgical treatment, adjuvant treatment, and tumor grade.
Keywords: survival, progression-free survival, Karnofsky Performance Status, glioma (source MeSH NLM)
RESUMEN
Introducción: Introducción: Los Gliomas son tumores primarios del sistema nervioso central. Son clasificados del I-IV grado, siendo los de alto grado el III y IV los más frecuentes y de pobre pronostico. Objetivo: Determinar los factores
pronósticos de supervivencia en pacientes por gliomas de alto grado en un hospital de Lima, Perú.
Objetivo: Determinar los factores pronósticos de supervivencia en pacientes por gliomas de alto grado en un hospital de Lima, Perú.
Métodos: Se revisaron retrospectivamente las historias clínicas con glioma de alto grado del 2010-2014, se analizaron diez variables; con graficas de supervivencia de Kaplan-Meier y Long-rank y el modelo de regresión de Cox.
Resultados: De un total de 278 pacientes con gliomas de alto grado 136 fueron varones y 142 mujeres. El análisis de la Supervivencia Libre de Progresión (SLP) tuvo un rango de 5,6-80,3 (mediana 22,7) y el análisis de supervivencia global
(PS) tuvo un rango de 4-83,2 (mediana 26,2) meses. La supervivencia global para el tumor de IV grado fue 15,7 meses (IC 95% 14,2-17,1); el III grado fue de 38,4 meses (IC 95% 35,8-40,9). El grado (PS: HR 15; SLP: HR 25,1); el tratamiento quirúrgico
(PS: HR 0,6; SLP: HR 0,49), edad (PS: HR 1,47; SLP: HR 1,7), tratamiento adyuvante (PS: HR 0,6; SLP: HR 0,58) y karnofsky (PS: HR 0,7) tuvieron correlación; mientras el Karnofsky para SLP no (P=0,146).
Conclusión: La edad, el estado funcional, el tratamiento quirúrgico, el tratamiento adyuvante y el grado del tumor son factores pronósticos de PS; en contraste, para SLP los factores pronósticos fueron la edad, tratamiento quirúrgico,
tratamiento adyuvante y el grado del tumor.
Palabras Clave: Supervivencia; Estado de ejecución de karnofsky; Glioma (fuente: DeCS BIREME).
Glioma is a primary tumor of the central nervous system and is classified in grades I-IV according to histopathological criteria (1), according to 2007 WHO classification criteria, grades III-IV are called high grade (two). )
The term "high-grade glioma" includes several tumor names such as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), anaplastic astrocytoma (AA), and anaplastic oligodendroglioma (OA). GBM is the most frequent tumor and corresponds to 80% of gliomas and the most aggressive, and affects approximately(2-3) people out of every 100,000 annually(3,4). However, the overall prognosis for glioma remains bad despite aggressive treatments, especially in patients with high-grade glioma, whose average survival time after surgery is only 12 to 15 months for glioblastoma and 2 to 5 years anaplastic glioma. (5,7)
Treatment of patients with high-grade gliomas remains a challenge for modern therapy. The prognosis of these patients is poor, the median patient survival after diagnosis is approximately 1 year(5,8). The need for histological diagnosis of tumor tissue in each case and the importance of decompression in symptomatic patients are well established, however, there is still controversy regarding the extent of surgical resection to be performed. Although many neurosurgeons recommend that gliomas can be resected as widely as possible (9,10), rigorous literature reviews have shown that there is little scientific evidence that aggressive surgical treatment significantly prolongs survival. (11,12)
br> The standard treatment for high-grade gliomas is multidisciplinary, but above all, the treatment is surgical(13,14). Total surgical resection is essential to increase patient survival, associated with chemotherapy and post-surgical adjuvant radiation therapy. In the past, surgical treatment was accompanied by important sequelae that led to low quality of life. Precisely, the maximum possible resection allows a better effect of radiotherapy in the control of the disease, increasing the survival of patients. Chemotherapy is part of the multidisciplinary management of gliomas, with an improvement in survival observed when associated with radiation therapy. (15,16)
Due to the fact that the survival factors in our environment are not yet clear, and the impact on health in the population is also uncertain, it is necessary to know a profile of patients with a greater and lesser chance of survival, for better decision-making, based on the evidence of our environment.
MÉTODOS .
Design and setting
Analytical, longitudinal, retrospective of survival. Performed in postoperative patients with high-grade glioma from the 2010-2014 period in the neurosurgery service of the Hospital Nacional Edgardo Rebagliati Martins.
Population and sample .
The population is all patients operated on for glioma, who were attended in the consulting room and emergency of the neurosurgery service of the Hospital Nacional Edgardo Rebagliati Martins.
Consecutive non-random sample. Information was collected from the medical records of the postoperative patients with high-grade glioma from the 2010-2014 period.
Inclusion criteria: 1) Patients older than 18 at the time of diagnosis; 2) Patients with a diagnosis of high-grade glioma confirmed by the pathological study, and 3) Patients who have undergone some type of surgical treatment.
Exclusion criteria: 1) Patients who have undergone more than one surgical intervention; and 2) Patients who have an incomplete imaging study; 3) Patients who have presented post-surgical complications inherent to the procedure, and 4) Incomplete medical records
Variables and instruments
Dependent variables
- Overall Survival (PS): These are the months of life from the time of surgery to death from the disease. The final expression was in months. It was measured through the logarithmic range method and the Cox proportional hazards regression analysis.
- Progression-free survival (PFS): These are the months of life from the moment of the surgical intervention until the reappearance of tumor recurrence. The final expression was in months. It was measured using the logarithmic range method and Cox proportional hazards regression analysis.
Independent variables
- Histological grade: Defined by the microscopic characteristics of the tumor tissue and classified according to the WHO, defined by the anatomic pathology report. In the study, it was measured in (1) grade III or (2) IV.
- Age: It is the lifetime of the patient taken since birth, which has been measured in years recorded on your health insurance. It was categorized into three stages: (1) 14-30 years; (2) 31-60 years; and (3)> 60 years.
- Gender: It is either male or female, as registered on your health insurance affiliation sheet (qualitative - nominal).
- Seizures: It is the generalized clonic tonic movement that is part of the symptomatic picture at the time of diagnosis. It was categorized as "yes" and "no" according to medical history.
- Ability to perform routine tasks: It is a way to quantify the ability of cancer patients to perform routine and/or daily tasks. For this, we will use the Karnofsky Performance Scale (KPS). It was categorized with a cutoff point "≥ 70" and "<70" according to what is recorded in medical history.
- Glioma location: It is the location of the tumor lesion in the cerebral hemisphere, visualized in cerebral magnetic resonance imaging. It was categorized into: (1) Frontal; (2) Parietal; (3) Occipital; (4) Temporary; (5) More than 1 area involved; and (6) Infratentorial.
- Tumor diameter: It is the measurement in centimeters of the largest diameter (in any dimension) on FLAIR images and / or T2 sequence of magnetic resonance imaging. It was categorized into (1) ≥ 5 cm and (2) <5 cm.
- Enveloping eloquent area: It is the location of the tumor in areas that dominate the sensory-motor functions (precentral and postcentral gyrus), language areas (upper temporal area, lower frontal area, and lower parietal area), basal ganglia, visual area (calcarine visual cortex). It was categorized as "yes" when it compromised these areas, and "no" if it did not.
- Surgical resection extension: It is the percentage of tumor extraction taking into account the pre-surgical and post-surgical images. It was categorized into: (1) Total; (2) Partial; and (3) Biopsy.
- Adjuvant Treatment: It is the presence of Radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy treatment after surgery. Evidenced in medical history by the sessions it received. It was categorized into: (1) RT / QT; (2) RT; and (3) No RT.
Patient Selection:
In the database of the archive of medical histories the Hospital Nacional Edgardo Rebagliati Martins, 200 histories of patients with high-grade glioma who received surgical treatment, craniectomy plus tumor excision, was chosen between the years 2010-2014. All patients present histological confirmation of high-grade glioma, grade III, and IV according to the classification system of the World Health Organization.
Acquisition of the variables:
The following data were obtained from the medical records of the patients: (1) Demographic Data (age and sex) and the ability to perform routine tasks (KFS) before the operation. (2)preoperative clinical symptoms: intracranial hypertension, irritation, and symptoms of nervous exhaustion and its duration. (3) Preoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): before the operation, MRI contrast was performed to determine if there was hemorrhage or necrosis of the tumor, tumor location, the extent of tumor invasion, and tumor size. The extent of tumor invasion is based on the number of lobes with high T2-weighted MRI signals(4). Treatment of: (a) surgical resection is the extent of tumor resection during operation by neurosurgeons and during the study of post-operative images analyzed by radiologists. Total resection of the tumor mass was less than 5% tumor residue (to protect important neurological functions). Subtotal resection was the removal of more than 80% of the tumor mass (b) Postoperative Radiotherapy is the postoperative radiotherapy which was given to patients at a routine dose: 40-60 Gy / 28 days to the tumor and edematous peripheral area 2 cm outside of it, plus 10 to 14 Gy applied to the region of the brain that surrounds 2 cm. (c) postoperative chemotherapy: standard chemotherapy (200 mg temozolomide / m2 body surface area) was administered 4-6 course of treatment and during radiotherapy, the temozolomide dose was halved. (5) Postoperative pathologic data: Based on pathologic examinations, patients were diagnosed with anaplastic astrocytoma, anaplastic oligodendroglioma, or anaplastic mixed glioma and with grades III and IV. (6) Follow-up data include disease outcomes with PS and SLP. Follow-up data was collected mainly when patients visited outpatient clinics and in telephone interviews with patients and / or family members. The rest of the data was obtained from medical records.
Study design:
Statistical analysis
The summary measures of the data were presented as means ± standard deviations for the parametric data and as medians with IQRs for non-parametric data. Statistical methods were performed with the SPSS v23.0 program. The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, the logarithmic range method, and the Cox proportional hazards regression analysis were used to analyze the effect of the different variables with time on PS and SLP. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Ethical aspects.
The data was collected by the study researchers. At the same time, permission was obtained from the hospital for the investigation. Finally, the information of the participants was delivered in a Microsoft Excel 2016 spreadsheet without biological identifiers, maintaining the confidentiality of the data.
RESULTS.
Of a total of 305 patients with high-grade gliomas, which were identified in the collected database, 278 patients met the inclusion criteria. Of these 136 were men and 142 women; the median age of the total was 51 years of age. The most frequent high-grade glioma was grade IV (51.4%). Most of the high-grade gliomas had supratentorial location (252 patients, 90.7%); 23.4% of the patients had their tumor located in eloquent areas; 65.5% of the patients had tumors with a diameter ≥ 5cm. The initial surgical treatment was resection in 95.7% of cases. Only 12 patients underwent biopsy. 174 (62.6%) patients presented a functional state greater than or equal to 70% on the Karnofsky scale. Headache was present in 69.1%. Furthermore, 20.5% of the patients presented with Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH). In the adjuvant treatment, 83.5% received radiotherapy and 60.8% received chemotherapy. The analysis of PFS time had a range of 5.6-80.3 with a mean of 22.7 months and the analysis of the follow-up of survival time had a range of 4-83.2 and a mean of 26.2 months .
Tumor grade, Karnofsky scale, surgical treatment, age, and adjuvant treatment were significantly associated with the PS that can be seen in Table No. 2 and Figure No. 1. The PS for the IV degree tumor was 15.7 months (95% CI 14.2-17.1) and for the III degree it was 38.4 months (95% CI 35.8-40.9); the patients under 60 years of age had a long PS of 32.6 months (P =0.015); for patients with a Karnofsky scale greater than 70%, they also presented 32.6 months of PS (95% CI 29.5-35.6); the patients with surgical treatment underwent total resection of the tumor, subtotal and biopsy, which had a PS of 30.8, 28.6 and 7.3 months, respectively; adjuvant radiotherapy/chemotherapy treatment had long PS (p <0.001). In the multivariate analysis, the tumor grade was the variable that had the highest correlation with PS (HR=1 5.5; p<0.001); while surgical treatment, age, adjuvant treatment, and karnofsky also correlated with PS (p=0 .07, p=0 .025, p=0.018, and p=0 .035 respectively) Table 4.
Table No. 3 and Figure No. 2. show the SLP analysis. The SLP for the IV degree tumor was 11.3 months (95% CI 10.3-12.2) while for the III degree it was 32.8 months (95% CI 29.4-36.1); for the PS it was 15.7 months (95% CI: 14.2-17.1) and 38.4 months (95% CI 35.8-40.9) respectively. In univariate analysis, SLP varies significantly with tumor grade, surgical treatment, age, Karnofsky scale, and adjuvant treatment. Patients with a cut point at 60 years had a significant variation in PFS (p= 0.01).
The multivariate analysis shown in Table 4 indicates that the tumor grade, surgical treatment, age, and adjuvant treatment were significantly correlated with PFS (p <0.001, p<0.001, p=0 .01 and p=0 .02 respectively) but no correlation was shown with the assessment of functional status (karnofsky scale).
Table 1. General characteristics of patients with high-grade glioma from the 2010-2014 period.
|
Variable |
n |
% |
|
Age |
|
|
|
14-30 |
35 |
12.6 |
|
31-60 |
150 |
54.0 |
|
61 and older |
93 |
33.5 |
|
Mean |
49 |
|
|
Sex |
|
|
|
Male |
136 |
48.9 |
|
Female |
142 |
51.1 |
|
Location of the Tumor |
|
|
|
Supratentorial |
|
|
|
Frontal |
58 |
20.9 |
|
Parietal |
60 |
21.6 |
|
Occipital |
10 |
3.6 |
|
Temporal |
52 |
18.7 |
|
More than 1 affected area |
72 |
25.9 |
|
Thalamus and Basal ganglia |
18 |
6.5 |
|
Infratentorial |
|
|
|
Brain stem |
2 |
0.7 |
|
Cerebellum |
6 |
1.7 |
|
Karnofsky |
|
|
|
≥ 70 |
174 |
62.6 |
|
<70 |
104 |
37.4 |
|
Eloquent area |
|
|
|
No |
213 |
76.6 |
|
Yes |
65 |
23.4 |
|
Tumor resection |
|
|
|
Total |
179 |
64.4 |
|
Subtotal |
87 |
31.3 |
|
Biopsy |
12 |
4.3 |
|
High-grade tumor |
|
|
|
Grade IV |
144 |
51.8 |
|
Grade III |
134 |
48.2 |
|
Tumor diameter |
|
|
|
<5 cm |
96 |
34.5 |
|
≥ 5 cm |
182 |
65.5 |
|
Symptoms |
|
|
|
Seizures |
84 |
30.2 |
|
Headache |
192 |
69.1 |
|
Hemiparesis |
85 |
30.6 |
|
Aphasia |
50 |
18.0 |
|
Dysarthria |
44 |
15.8 |
|
IIH |
57 |
20.5 |
|
Others |
52 |
18.7 |
|
Adjuvant treatment |
|
|
|
RT/QT |
162 |
58.3 |
|
RT |
71 |
25.5 |
|
NO RT |
45 |
16.2 |
Table 2. Median overall survival by a group of patients with high-grade glioma from the 2010-2014 period.
|
Variable |
Median (months) |
95% CI |
p ** |
|
Degree of Tumor |
|
|
|
|
Grade IV |
15.7 |
14.2 - 17.1 |
<0.001 |
|
Grade III |
39.4 |
35.8 - 40.9 |
|
|
Gender |
|
|
|
|
Male |
36.4 |
20.2 - 32.5 |
0.59 |
|
Female |
30.8 |
24.1 - 37.4 |
|
|
Clinical Manifestations |
|
|
|
|
Seizures |
32.1 |
26.8 - 37, 3 |
0.54 |
|
IIH |
29.5 |
21.1 - 35.4 |
0.82 |
|
Karnofsky |
|
|
|
|
≥ 70% |
32.6 |
39.5 - 35.6 |
0.005 |
|
<70% |
21.4 |
13.0 - 37.8 |
|
|
Tumor Diameter |
|
|
|
|
≥ 5 cm |
24.7 |
17.3 - 32.0 |
0.54 |
|
<5 cm |
30.8 |
26.1 - 35.4 |
|
|
Type of surgical treatment |
|
|
|
|
Total |
30.8 |
25.0 - 36.5 |
<0.001 |
|
Subtotal |
20.60 |
18 , 2 - 38.9 |
|
|
Biopsy |
7.3 |
4.6 - 9.9 |
|
|
tumor |
|
|
|
|
Supratentorial location |
29.6 |
24.6 - 34.5 |
0.56 |
|
Basal ganglia and thalamus |
22.8 |
8.1 - 37.4 |
|
|
Infratentorial |
12 , 3 |
7.4 - 17.1 |
|
|
Age |
|
|
|
|
<60 years |
32.6 |
29.2 - 35.9 |
0.015 |
|
≥ 60 years |
22.4 |
17.5 - 27.2 |
|
|
Eloquence |
|
|
|
|
Yes |
32.8 |
27.4 - 38.1 |
0 , 43 |
|
No |
26.4 |
21.3 - 31.4 |
|
|
Adjuvant Treatment |
|
|
|
|
RT / QT |
32.9 |
30.1 - 35.6 |
<0.001 |
|
RT |
26.4 |
14.2 - 38.5 |
|
|
NO RT |
12.6 |
10.7 - 14.4 |
|
Table 3. Median progression-free survival by groups of patients with high-grade glioma for the period 2010-2014
|
Variable |
Median (months) |
95% CI |
p ** |
|
Degree of Tumor |
|
|
|
|
Grade IV |
13.3 |
10.3 - 12.2 |
<0.001 |
|
Grade III |
32.8 |
29.4 - 36.1 |
|
|
Gender |
|
|
|
|
Male |
20.4 |
12.2 - 29.5 |
0.61 |
|
Female |
24.8 |
17.9 - 31.6 |
|
|
Clinical Manifestations |
|
|
|
|
Seizures |
28.6 |
21.5 - 35.6 |
0.57 |
|
IIH |
25.7 |
14.2 - 37.1 |
0.961 |
|
Karnofsky |
|
|
|
|
≥ 70% |
29.7 |
25.1 - 34.2 |
0.045 |
|
<70% |
14 , 6 |
9.9 - 19.2 |
|
|
Tumor Diameter |
|
|
|
|
≥ 5 cm |
20.8 |
14.1 - 27.5 |
0.62 |
|
<5 cm |
27.9 |
21.7 - 34.0 |
|
|
Type of surgical treatment |
|
|
|
|
Total |
28.3 |
25 , 0 - 36.5 |
<0.001 |
|
Subtotal |
20.4 |
8.9 - 31.8 |
|
|
Biopsy |
- |
- |
|
|
Tumor location |
|
|
|
|
Supratentorial |
24.8 |
18.8 - 30.7 |
0.58 |
|
Basal ganglia and thalamus |
20.4 |
14.5 - 25.7 |
|
|
Infratentorial |
10.0 |
5.4 - 14.5 |
|
|
Age |
|
|
|
|
<60 years |
28.6 |
23.4 - 33.7 |
0.01 |
|
≥ 60 years |
15.4 |
9.5 - 21.2 |
|
|
Eloquence Area |
|
|
|
|
Yes |
28.3 |
18 , 9 - 37.6 |
0.465 |
|
No |
22.6 |
15.5 - 29.6 |
|
|
Adjuvant Treatment |
|
|
|
|
RT/QT |
30.4 |
28.5 - 32.2 |
<0.001 |
|
RT |
14.9 |
11.1 - 18, 6 |
|
|
NO RT |
9 |
7.6 - 10.3 |
|
Table 4. Multivariate analysis with the COX proportional hazards ratio model for progression-free survival (SLP) and overall survival (PS).
|
|
SLP |
PS |
||||
|
Variable |
HR Adjusted |
95% CI |
P ** |
HR Adjusted |
95% CI |
P ** |
|
Tumor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grade IV |
Ref. |
|
|
Ref. |
|
|
|
Grade III |
25.1 |
14.6 - 42.9 |
<0.001 |
15.5 |
9.4 - 25.4 |
<0, 01 |
|
Surgical Treatment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
Ref. |
|
|
Ref. |
|
|
|
Subtotal |
0.49 |
0.33 - 0.70 |
<0.001 |
0.6 |
0.41 - 0.87 |
0.07 |
|
Age |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<60 years |
Ref. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
≥ 60 years |
1.7 |
1.23 - 2.44 |
0.02 |
1.47 |
1.4 - 2.07 |
0.025 |
|
Adjuvant Treatment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RT / QT |
Ref. |
|
|
Ref. |
|
|
|
RT |
0.58 |
0.41 - 0.81 |
0.02 |
0.667 |
0.47 - 0.93 |
0.018 |
|
Karnofsky |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
≥ 70% |
Ref. |
|
|
Ref. |
|
|
|
<70% |
1.3 |
0.91 - 1.88 |
0.146 |
0.7 |
0.52 - 0.97 |
0.035 |
** p-value obtained through the Log Rank test
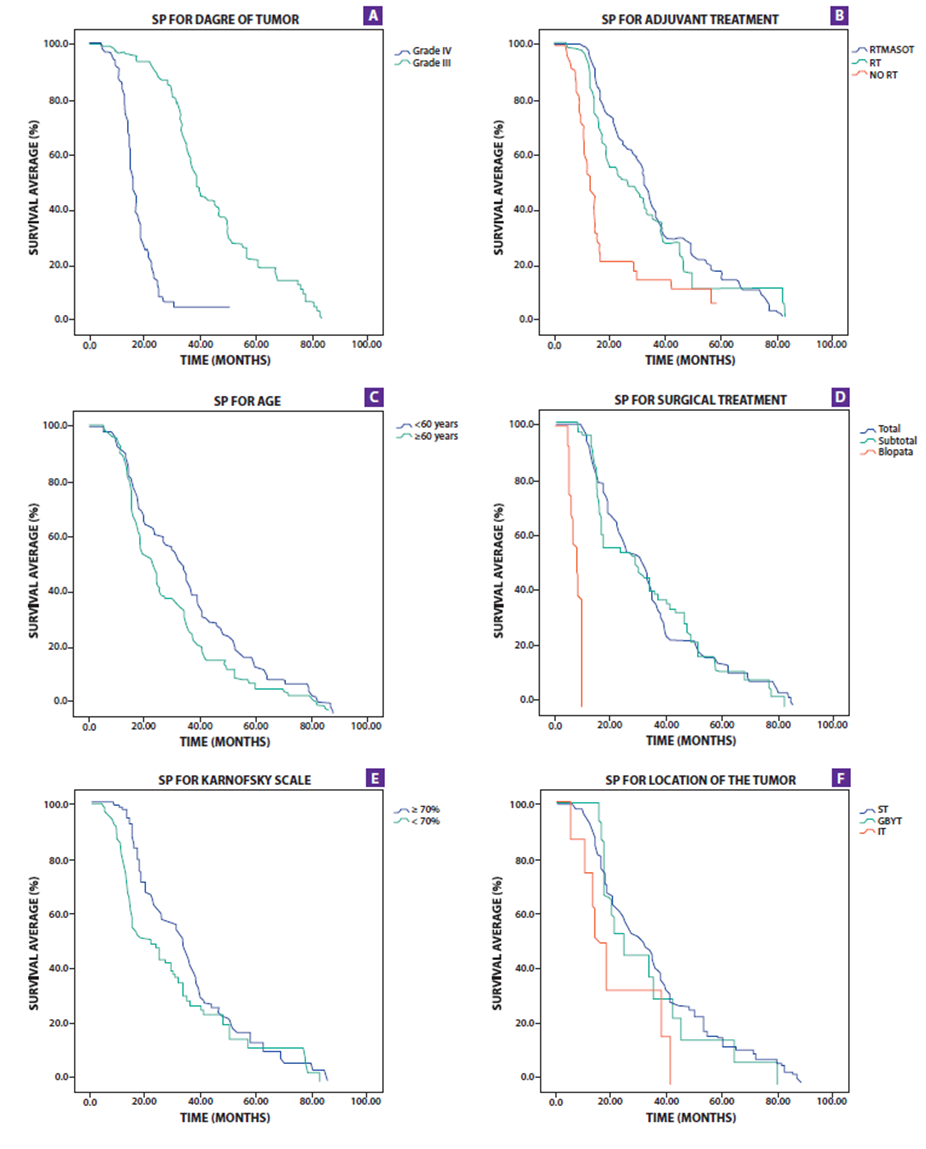
Figure 2. Survival charts showing overall survival (PS) by tumor grade (A), Adjuvant Treatment (B), age (C), Surgical Treatment (D), Karnosfsky (E) and Tumor location (F).

Figure 3. Graphics of survival showing progression-free survival (PFS) by tumor grade (A), Adjuvant Treatment (B), age (C), Surgical Treatment (D), Karnofsky (E), and Tumor location (F).
Glioblastoma multiforme (IV degree tumor) is the most aggressive primary neoplasm of the central nervous system. This neoplasm occurs mainly between 60 and 70 years old. In the present study, the median age of the patients was 51 years, which is consistent with the studies by McGirt and Liang. (17,18)with a median of 54 years. Furthermore, patients with a range greater than or equal to 60 years had lower average survival. Similar data were found in the studies by Yong-jian (19)and Lacroix for age ≥ 65 years (20)and lower progression-free survival .
Men represent the largest number of patients with high-grade glioma; however, in our study, there was no correlation with PS or SLP. (8,19,21) .
As the most frequent clinical manifestation in our study was a headache, followed by seizures and motor deficit (13,22,23), however, none of them was related to patient survival; unlike Liang's study, in which he found an association in survival, by separating symptoms that do or do not belong to the picture of intracranial hypertension.
In our study, the Karnofsky scale (KFS) was used to assess the functional state of the patient, which was considered a good functional state at a KFS≥70, which was the most frequent and was correlated with better survival (median of 32, 6 months) (24), other studies such as Lacroix and Chaichana reported similar results but with a KFS ≥80(20,23). No association was found regarding PFS .
IV grade tumors, called glioblastoma multiforme, are the tumors with the shortest survival time, so in our study, the PS was 15.7 months, these are corroborated in the literature with many studies (17,18,20,22-25)and in terms of PFS was 11.3 months, similar to the results of Ahmadloo (22) in a series of 223 patients; III degree tumor, called anaplastic gliomas, the survival was 38.4 months and PFS was 32.8, similar findings to the Nuño study(26); According to the data from our study, the grade of the tumor is a strong prognostic factor .
The location of the tumor is another of the variables that have been evaluated in our study, where tumors of the supratentorial location were the most frequent, and of these tumors that had more than 1 affected area, the parietal and frontal region were the most frequent. affected (18), however, there was no correlation with the PS or the SLP (22,23,27), unlike Kumar, who found an association between the location of the tumor (parietal lobe) and survival(4). In our study we also evaluated the location of the tumor in an eloquent area, most of the tumors were not in these areas and there was also no correlation with PS and PFS, similar results exist in the literature (20,23). Few studies take the variable diameter of the tumor with a cut point between 4 or 5 cm in diameter, our study used the latter, without finding a correlation (19,22,24).
As for the treatment of tumors, the surgical option remains the choice for the management of this pathology, with total or near-total resection providing the best PS (median of 30.8 months) when compared to the subtotal (median of 20.6 months) or biopsy (median of 7 months) In addition, it forms a good prognostic factor (23,24).similar to most studies; thus, it also influences PFS with a median of 28.3 and 20.4 for total and subtotal resection, respectively (22,23).. Adjuvant treatment with radiotherapy and chemotherapy or a combination of these improves the average survival and PFS, as well as being a good prognostic factor (22,23).; at this point in reference, it coincides with many of the published studies .
There are some limitations to the study to consider. First, the study population is only from a hospital, so extrapolating all these results to the population may not be completely recommended; however, since the hospital is a place where most cases arrive from all over the country, some inference can be made, and the results should not vary in the magnitude of the result. Then, we can consider Berkson's bias, which tells us about the impact of working with people enrolled in a hospital; But, as this is a single-arm study, looking only at the prognostic factors for high-grade glioma, its impact on the outcome should not be significant. .
CONCLUSION: .
According to the data in our study, age, functional status, surgical treatment, adjuvant treatment, and tumor grade are prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with high-grade glioma. In contrast to progression-free survival, prognostic factors were age, surgical treatment, adjuvant treatment, and tumor grade.
Author's contribution: The authors participated in the genesis of the idea, project design, data collection and interpretation, analysis of results, and preparation of the manuscript of the present research work.
Funding sources:Self-financed.
Conflicto de interés: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Received:June 26,2020
Approved:July 12, de 2020
Correspondence: Víctor Juan Vera Ponce.
Address: Universidad Ricardo Palma. Av. Alfredo Benavides 5440, Santiago de Surco, Lima-Perú.
Telephone number: + 51 940072431
E-mail: victor_jvp@hotmail.com
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES