Sturge Weber syndrome, classic triad from a genetic, molecular and physiological approach
Síndrome de Sturge Weber, triada clasica desde un enfoque genético, molecular y fisiopatológico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.25176/RFMH.v20i3.2974Keywords:
Sturge-Weber Syndrome, Genetics, physiopathologyAbstract
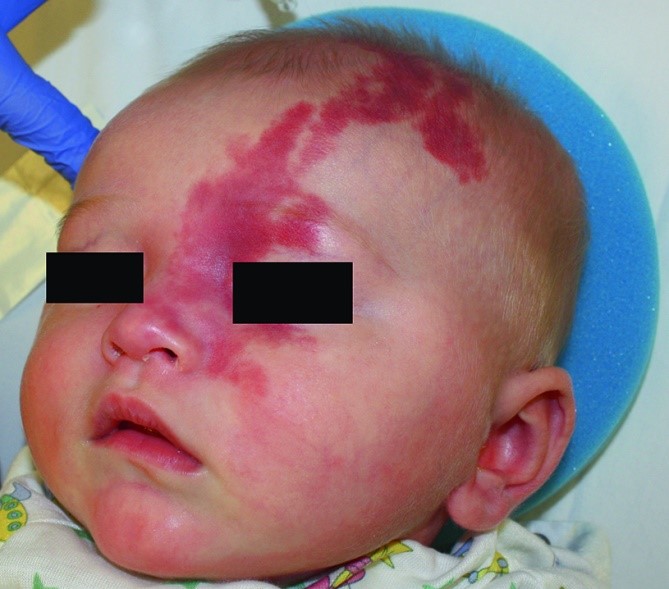
Sturge Weber syndrome (SSW) is characterized by the classic involvement of sporadic neuro-oculo-cutaneous vascular malformations, the pathophysiology of which to date has not been fully elucidated.The discovery of both an arterial and venous molecular profile in the endothelium present in vascular malformations, together with vascular atresia zones distal to the ectatic zones, have led to questioning the embryological theories put forward for decades, to explore the molecular and genetic characteristics in the affected tissue.
Currently, a high prevalence of somatic mutation in the GNAQ gene has been reported in the affected tissues of patients with SSW, which encodes an alpha subunit of a Gq protein, whose signaling cascade stimulates cell proliferation, which may be responsible of the sustained growth of malformations in the three mentioned regions. The present study aims to explain the classic clinical manifestations of SSW from a genetic, molecular and pathophysiological perspective.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Revista de la Facultad de Medicina Humana

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



































