Acute pneumonitis after subcutaneous injection of BIO-ALCAMID® in breast
Neumonitis aguda secundaria a la inyección subcutánea de gel de polialquilamida (BIO-ALCAMID) en mamas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.25176/RFMH.v23i1.4992Keywords:
Acute pneumonitis, biopolymer, filler material, dyspneaAbstract
ABSTRACT:
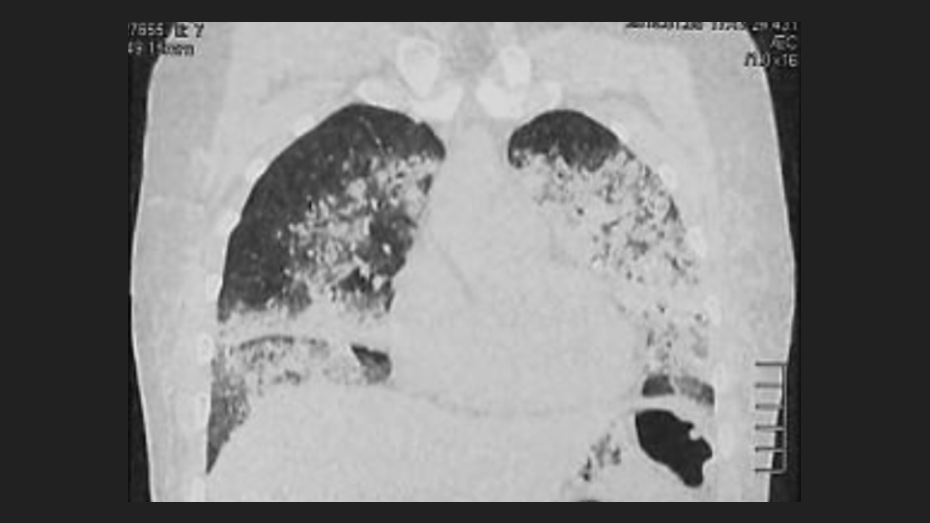
Filling materials are used to correct soft tissue deficits. Local and systemic complications are described when these substances are applied. The polyalkylamide gel (Bio-alcamid) used as filler material has been associated with complications at the facial level, while at the pulmonary level they have not been reported in the literature. We present the case of a patient who consulted due to sudden progressive dyspnea hours after the subcutaneous injection of Bio-alcamid in the breasts. After the clinical evaluation and the result of auxiliary tests, the diagnosis of acute pneumonitis secondary to the injection of this substance is concluded. Follow-up of the case was carried out with favorable evolution and resolution of symptoms after three months. We conclude that Bio-alcamid can generate complications at the pulmonary level, therefore, the intervention of public policies that regulate its use, commercialization and application by non-medical personnel is necessary.
Downloads
References
Aguilar Donis A, García Gutiérrez P, Rebollo Domínguez N, Segura Moreno G, Ruiz Ávila J. Revisión de materiales de relleno. Vol. 13, Dermatología Cosmética, Médica y Quirúrgica. 2015 Feb.
SCHELKE LW, VAN DEN ELZEN HJ, CANNINGA M, NEUMANN MHA. Complications after Treatment with Polyalkylimide. Dermatologic Surg [Internet]. 2009 Oct [cited 2020 Oct 2];35(SUPPL. 2):1625–8. Available from: http://journals.lww.com/00042728-200910002-00006
Chung KY, Kim SH, Kwon IH, Choi YS, Noh TW, Kwon TJ, et al. Clinicopathologic Review of Pulmonary Silicone Embolism with Special Emphasis on the Resultant Histologic Diversity in the Lung: A Review of Five Cases. Yonsei Med J [Internet]. 2002 Apr 1 [cited 2020 Oct 2];43(2):152. Available from: https://eymj.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3349/ymj.2002.43.2.152
Chastre J, Basset F, Viau F, Dournovo P, Bouchama A, Akesbi A, et al. Acute Pneumonitis after Subcutaneous Injections of Silicone in Transsexual Men. N Engl J Med [Internet]. 1983 Mar 31 [cited 2020 Oct 2];308(13):764–7. Available from: http://www.nejm.org/doi/abs/10.1056/NEJM198303313081307
Goldblum RM, O’Donell AA, Pyron D, Goldblum RM, Pelley RP, O’Donell AA, et al. Antibodies to silicone elastomers and reactions to ventriculoperitoneal shunts. Lancet [Internet]. 1992 Aug 29 [cited 2020 Oct 2];340(8818):510–3. Available from: http://www.thelancet.com/article/014067369291710P/fulltext
Nadarajah JT, Collins M, Raboud J, Su D, Rao K, Loutfy MR, et al. Infectious complications of bio-alcamid filler used for HIV-related facial lipoatrophy. Clin Infect Dis [Internet]. 2012 Dec 1 [cited 2020 Oct 2];55(11):1568–74. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/55/11/1568/370433
Nelson L, Stewart KJ. Early and late complications of polyalkylimide gel (Bio-Alcamid)®. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg [Internet]. 2011 Mar [cited 2020 Sep 30];64(3):401–4. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1748681510002652
Alicia Gutiérrez Padilla R, de los Ángeles Flores Morales L, no Alonso Martínez D, Mateos Toledo H, Octavio Gaxiola Gaxiola M, Mayra Edith Mejía Ávila I. Neumonitis aguda secundaria a la inyección subcutánea de biopolímero líquido [Internet]. Vol. 70, Neumol Cir Torax. Medigraphic; 2011 [cited 2020 Oct 2]. Available from: www.medigraphic.org.mx
Pastor E, Andreu AL, Chiner E. Neumonitis aguda y síndrome de distrés respiratorio del adulto tras inyección subcutánea de silicona líquida. Arch Bronconeumol [Internet]. 2005 Dec 1 [cited 2020 Oct 2];41(12):702–3. Available from: https://www.archbronconeumol.org/es-neumonitis-aguda-sindrome-distres-respiratorio-articulo-13082592
Chastre J, Brun P, Soler P, Basset F, Trouillet JL, Fagon JY, et al. Acute and latent pneumonitis after subcutaneous injections of silicone in transsexual men. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987;135(1):236–40.
Narins RS, Beer K. Liquid injectable silicone: A review of its history, immunology, technical considerations, complications, and potential [Internet]. Vol. 118, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg; 2006 [cited 2020 Oct 2]. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16936547/
Parikh R, Karim K, Parikh N, Han P, Joseph D, Han Shamoon FE. Acute Pneumonitis and Alveolar Hemorrhage after Subcutaneous Injection of Liquid Silicone. Ann Clin Lab Sci [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2020 Oct 2];38(4):380–5. Available from: http://www.annclinlabsci.org/content/38/4/380.long
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista de la Facultad de Medicina Humana

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



































