INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION DUE TO STRONGYLOIDES STERCOLARIS: ABOUT A CASE.
OBSTRUCCIÓN INTESTINAL POR STRONGYLOIDES STERCOLARIS: A PROPÓSITO DE UN CASO
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.25176/RFMH.v23i4.5912Keywords:
Strongyloides stercoralis, ivermectin, cachexia, hyperinfection syndromeAbstract
ABSTRACT
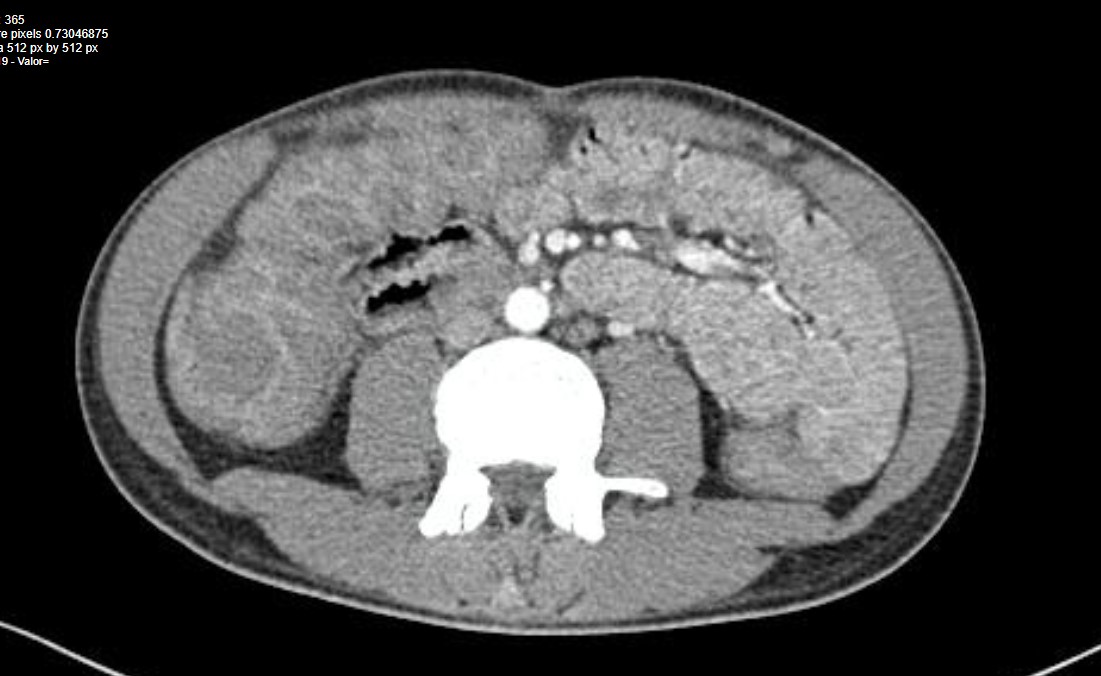
Strongyloidiasis commonly causes gastrointestinal problems. We present the case of a male, a 30-year-old cadet in the Peruvian Navy from Lima, who developed a hyperinfection syndrome due to Strongyloides stercoralis, having a presumptive diagnosis of polymyositis for which he received a short cycle of corticosteroids. He was not a carrier of the HTLV 1/2 virus. Upon admission, he presented with hyporexia, generalized weakness, cachexia, intermittent self-limited diarrhea, oral intolerance, and mild abdominal distension. The patient reached the dissemination stage, resulting in severe intestinal damage. The low excretion of larvae in the feces made the diagnosis difficult. Treatment was provided with parenteral ivermectin at a dose of 1.2ml subcutaneously every 48 hours for three doses, with a good clinical response and subsequently good oral tolerance. The importance of presenting the case is to comment on the diagnostic and therapeutic approach to this endemic geohelminthiasis of Peru.
Downloads
References
Krolewiecki A, Nutman TB. Strongyloidiasis: a neglected Neglected Tropical Disease (NTD). Infect Dis Clin North Am. marzo de 2019;33(1):135-51.
Ortiz-Martínez S, Ramos-Rincón JM, Vásquez-Chasnamote ME, Gamboa-Paredes ON, Arista-Flores KM, Espinoza-Venegas LA, et al. Prevalence of strongyloidiasis in Peru: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 4 de agosto de 2021;21:755.
Soto-Febres F, Pérez-Lazo G, Anicama W, Maquera-Afaray J. Obstrucción duodenal por Strongyloides stercoralis, una complicación inusual. Rev Chil Infectol. febrero de 2019;36(1):101-5.
Rothe K, Katchanov J, Schneider J, Spinner CD, Phillip V, Busch DH, et al. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome presenting as mechanical ileus after short-course oral steroids for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation. Parasitol Int. junio de 2020;76:102087.
Zeitler K, Jariwala R, Restrepo-Jaramillo R, Kapadia S, Casanas B, Alrabaa S, et al. Successful use of subcutaneous ivermectin for the treatment of Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection in the setting of small bowel obstruction and paralytic ileus in the immunocompromised population. BMJ Case Rep. 4 de junio de 2018;bcr-2017-223138.
Barrett J, Broderick C, Soulsby H, Wade P, Newsholme W. Subcutaneous ivermectin use in the treatment of severe Strongyloides stercoralis infection: two case reports and a discussion of the literature. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1 de enero de 2016;71(1):220-5.
Romero-Cabello R, Villagroy Gómez J, Hernández González M, Romero Feregrino R. Hyperinfection with Strongyloides stercoralis. BMJ Case Rep. 30 de noviembre de 2012;2012:bcr2012006819.
Rothe K, Katchanov J, Schneider J, Spinner CD, Phillip V, Busch DH, et al. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome presenting as mechanical ileus after short-course oral steroids for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation. Parasitol Int. 1 de junio de 2020;76:102087.
El Hajj W, Nakad G, Abou Rached A. Protein Loosing Enteropathy Secondary to Strongyloidiasis: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2016;2016:6831854.
Chen YA, Hsu HM, Wang H, Lan HH, Huang SH, Hung CC, et al. Epidemiology, clinical features, and outcomes of strongyloidiasis in Taiwan from 1988 to 2020: A case series and literature review. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. febrero de 2023;56(1):172-81.
Martyn E, Gration B, Subbiah Somasundaram C, Chiodini PL. Strongyloides, HTLV-1 and small bowel obstruction. BMJ Case Rep. 9 de diciembre de 2019;12(12):e232461.
Hennessey DC, Ballesteros ÓA, Merchán DJ, Guevara FO, Severiche DF. Ivermectina subcutánea en el tratamiento de un síndrome de hiperinfección por Strongyloides stercoralis. Biomédica. 15 de junio de 2020;40(2):228-32.
Cuadros-Mendoza CA, Lozano-Agudelo K, Otoya-Castrillon JP, Serrato-Roa F, Navarro-Mejia YA. Severe gastroduodenitis due to Strongyloides stercoralis infection: An unusual cause of intestinal obstruction. Rev Gastroenterol México Engl Ed. 1 de abril de 2023;88(2):188-90.
Paz Rojas E, Cerrón Cabezas C, Cruz Touzet J, Delgado Gonzales V, Gonzales-Hamada L, Maguiña Vargas C, et al. Infección diseminada por Strongyloides stercoralis en dos receptores de trasplante renal de un único donante. Acta Médica Peru. julio de 2017;34(3):225-30.
Patra AA, Nath P, Pati GK, Panigrahi SC, Mallick B, Acharya JCK, et al. Strongyloides Infection Presenting as Proximal Small Intestinal Obstruction. ACG Case Rep J. 25 de junio de 2019;6(6):e00124.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Revista de la Facultad de Medicina Humana

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



































