(Uveitis - glaucoma - hyphema syndrome: Clinical case)
Síndrome de uveitis - glaucoma - hifema: Caso clínico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.25176/RFMH.v23i3.5699Keywords:
Uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema syndrome, intraocular lens, sulcus, capsular bagAbstract
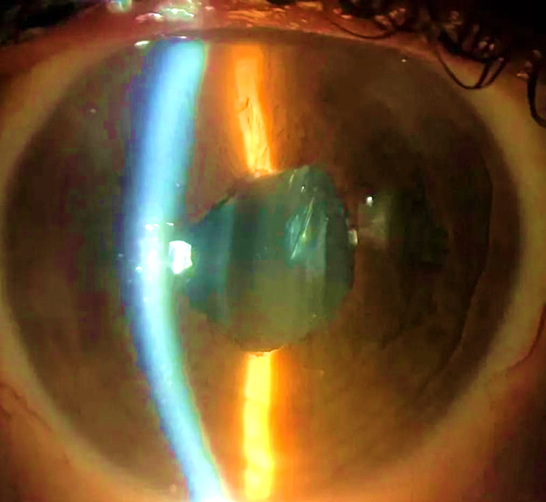
Introduction: Uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema syndrome (UGH) is a rare complication of cataract surgery, due to mechanical chafing exerted by an intraocular lens (IOL) on the iris. Clinical case: We present the case of a 64-year-old man with a history of cataract surgery, who presented decreased visual acuity and pain in the right eye. The ophthalmological examination revealed signs of anterior uveitis, elevated intraocular pressure (IOP), microhyphema, and a single-piece foldable IOL in the sulcus that caused a mechanical chafing with the posterior face of the iris. The medical treatment was insufficient, for this reason a folding simple-piece IOL explant surgery was performed and replaced by a three-piece IOL. Postoperative evolution was favorable. Conclusion: We should suspect this complication in patients with a history of cataract surgery, especially in cases in which the IOL is in single-piece and has been implanted outside the capsular bag.
Downloads
References
Accorinti M, Saturno M, Paroli M, et al. Uveitis-Glaucoma-Hyphema Syndrome: Clinical Features and Differential Diagnosis. Ocul Inmunol Inflamm. 2021;1:1-6. https://doi.org/10.1080/09273948.2021.1881563
Yang J, Qiu X, Cai L, et al. Uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema syndrome associated with an in-the-bag square-edge intraocular lens. Precis Clin Med. 2019;2(4):283-287. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcmedi/pbz026
Mammo D, Page M, Olson J. Yoga-induced uveitis glaucoma hyphema syndrome. Digit J Ophthalmol. 2020:26(4):46-48. DOI: 10.5693/djo.02.2020.11.001
Du Y, Zhu X, Yang J, et al. Uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema syndrome with sclera-fixed posterior-chamber two-haptic intraocular lens in a highly myopic eye: a case report. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020;20(22):1-5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-020-1309-5
Zemba M, Camburu G. Uveitis-Glaucoma-Hyphaema Syndrome. General review. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2017;61(1):11-17. DOI:10.22336/rjo.2017.3
Alfaro A, Vital C, Sanchez J, et al. Uveitis-glaucoma-hyphaema syndrome associated with recurrent vitreous hemorrhage. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2015;90:392-394. DOI: 10.1016/j.oftale.2015.08.007
Piette S, Canlas O, Tran H, et al. Ultrasound biomicroscopy in uveitis-glaucoma- hyphema syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002;133(6):839-841. DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9394(02)01386-7
Smith T, Cheung A, Hart J, Chen C. Uveitis, glaucoma, hyphema syndrome: A referral-based, retrospective analysis. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57(12):1-10.
Nath S, Rai A. Uveitis–glaucoma–hyphema syndrome after uneventful placement of a 1-piece intraocular lens into the capsular bag. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2022;10(1):1-3. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.jcro.0000000000000064
Singh H, Modabber M, Safran S, Ahmed l. Laser iridotomy to treat uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema syndrome secondary to reverse pupillary block in sulcus-placed intraocular lenses: Case series. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015;41(10):2215-2223. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2015.10.057
Zhang L, Hood C, Vrabec J, et al. Mechanisms for in-the-bag uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema syndrome. J Cataract Refract. Surg. 2014;40(3):490-492. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2013.12.002
Le T, R Doug, Sozeri Y. Uveitis-Glaucoma-Hyphema Syndrome: a Review and Exploration of New Concepts. Curr Ophthalmol Rep. 2020;8(3):1-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40135-020-00233-1
El Wardani M, Kymionis G, Salmon B, et al. Uveitis-Glaucoma-Hyphema Syndrome Treated with Haptic Amputation. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2019;236(4):581-583. DOI: 10.1055/a-0829-6036
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista de la Facultad de Medicina Humana

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


































